Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
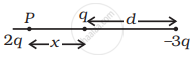
Two charges q and – 3q are placed fixed on x-axis separated by distance ‘d’. Where should a third charge 2q be placed such that it will not experience any force?
उत्तर
At P: on 2q, Force due to q is to the left and that due to –3q is to the right.
∴ `(2q^2)/(4 piε_0 x^2) = (6q^2)/(4 piε_0 (d + x)^2`
∴ `(d + x)^2 = 3x^2`
∴ `2x^2 - 2dx - d^2` = 0
`x = d/2 + (sqrt(3)d)/2`
(–ve sign would be between q and – 3q and hence is unacceptable.)
`x = d/2 + (sqrt(3)d)/2 = d/2 (1 + sqrt(3))` to the left of q.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table of Physical Constants and determine the value of this ratio. What does the ratio signify?
Four point charges qA = 2 μC, qB = −5 μC, qC = 2 μC, and qD = −5 μC are located at the corners of a square ABCD of side 10 cm. What is the force on a charge of 1 μC placed at the centre of the square?
Suppose that the particle is an electron projected with velocity vx = 2.0 × 106 m s−1. If E between the plates separated by 0.5 cm is 9.1 × 102 N/C, where will the electron strike the upper plate? (|e| = 1.6 × 10−19 C, me = 9.1 × 10−31 kg)
Suppose an attractive nuclear force acts between two protons which may be written as F=Ce−kr/r2. Write down the dimensional formulae and appropriate SI units of C and k.
Two charged particles with charge 2.0 × 10−8 C each are joined by an insulating string of length 1 m and the system is kept on a smooth horizontal table. Find the tension in the string.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C and a mass of 100 g is placed at the bottom of a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30°. Where should another particle B, with the same charge and mass, be placed on the incline so that it may remain in equilibrium?
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. If it is displaced through a distance x perpendicular to AB, what would be the electric force experienced by it?
Polarised dielectric is equivalent to ______.
A charge Q is divided into two parts of q and Q – q. If the coulomb repulsion between them when they are separated is to be maximum, the ratio of Q/q should be ______.
Four charges equal to −Q are placed at the four a corners of a square and charge q is at its centre. If the system is in equilibrium, the value of q is ______.
