Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In figure, a body A of mass m slides on plane inclined at angle θ1 to the horizontal and µ1 is the coefficent of friction between A and the plane. A is connected by a light string passing over a frictionless pulley to another body B, also of mass m, sliding on a frictionless plane inclined at angle θ2 to the horizontal. Which of the following statements are true?
- A will never move up the plane.
- A will just start moving up the plane when `µ = (sin θ_2 - sin θ_1)/(cos θ_1)`
- For A to move up the plane, θ2 must always be greater than θ1.
- B will always slide down with constant speed.

उत्तर
b and c
Explanation:
This system can be represented by the figure given below.
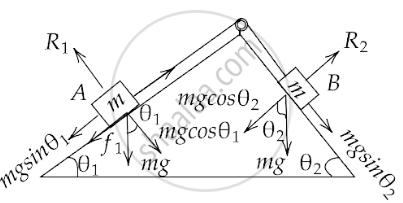
Here we have `f = μmg cos θ_1`
Now, body A will move up and body B will move down the plane,
If `mg sin θ_1 + f = mg sin θ_2`
That gives us, `mg sin θ_1 + μmg cos θ_1 = mg sin θ_2`
Or, `μ cos θ_1 = sin θ_2 - sin θ_1`
Hence, `μ = s (hati nθ_2 - sin θ_1)/(cos θ_1)`
Also, body A will move down and body B will move up the plane,
If `mg sin θ_2 - mg sin θ_1 > 0`
Or, `sin θ_2 > sin θ_1`
Hence, θ2 > θ1.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a cork of mass 10 g floating on water.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a kite skillfully held stationary in the sky.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a car moving with a constant velocity of 30 km/h on a rough road.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a high-speed electron in space far from all material objects, and free of electric and magnetic fields.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass 0.1 kg, just after it is dropped from the window of a stationary train. Neglect air resistance.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass 0.1 kg, just after it is dropped from the window of a train running at a constant velocity of 36 km/h. Neglect air resistance.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass 0.1 kg, just after it is dropped from the window of a train accelerating with 1 m s–2. Neglect air resistance.
Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on a stone of mass 0.1 kg, lying on the floor of a train which is accelerating with 1 m s–2, the stone being at rest relative to the train. Neglect air resistance.
Explain why passengers are thrown forward from their seats when a speeding bus stops suddenly.
A cricket bowler releases the ball in two different ways
- giving it only horizontal velocity, and
- giving it horizontal velocity and a small downward velocity. The speed vs at the time of release is the same. Both are released at a height H from the ground. Which one will have greater speed when the ball hits the ground? Neglect air resistance.
