Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are ______.
विकल्प
Perpendicular to each other.
Non-parallel to each other.
Parallel to each other.
Intersecting each other.
उत्तर
In the refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are parallel to each other.
Explanation:
For refraction to happen the light ray will have to incident obliquely. If the light ray is incident on the glass slab at a zero angle of incidence the ray will travel without any change of direction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is refraction of light?
Name the phenomenon responsible for the following effect:
When we sit in front of a plane mirror and write with our right hand, if appears in the mirror that we are writing with the left hand.
State whether the following statement is true of false:
A student says that we can see an object because light from our eyes is reflected back by the object.
The letter F is placed in front of a plane mirror:
How would its image look like when seen in a plane mirror?
Explain why, though both a plane mirror and a sheet of paper reflect light but we can see the image of our face in a plane mirror but not in a sheet of paper.
The image of an object formed by a plane mirror is:
(a) virtual
(b) real
(c) diminished
(d) upside-down
The figure given alongside shows the image of a clock as seen a plane mirror. The correct time is:
Figure
(a) 2.25
(b) 2.35
(c) 6.45
(d) 9.25
An object is placed 20 cm in front of a plane mirror. The mirror is moved 2 cm towards the object. The distance between the positions of the positions of the original and final images seen in the mirror is ______.
A man sits in an optician's chair looking into plane mirror which is 2 m away from him and views the image of a chart which faces the mirror and is 50 cm behind his head. How far away from his eyes does the chart appear to be?
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror PQ at an angle of incidence of 30°, is reflected from the plane mirror and then strikes a second plane mirror QR placed at right angles to the first mirror. The angle of reflection at the second mirror is ______.
If a ray of light goes form a denser medium to a rarer medium, will it bend towards the normal or away from the normal?
A ray of light travelling in glass emerges into air. State whether it will bend towards the normal or away from the normal.
State two effects caused by the refraction of light.
When a ray of light passes from air into glass, is the angle of refraction greater than or less than the angle of incidence?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
Refraction occurs because light slows down in denser materials.
Why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium to another?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Light bends when is passes from water into air. We say that it is ............
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a rectangular glass block and emerges out into the air from the opposite face. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the completer path of this ray of light. Mark the two points where the refraction of light takes place. What can you say about the final direction of ray of light?
What is meant by the 'angle of incidence' and the 'angle of refraction' for a ray of light?
Light travels more quickly through water than through glass.
Which is optically denser : water or glass?
Light travels more quickly through water than through glass.
If a ray of light passes from glass into water, which way will it bend : towards the normal or away from the normal?
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain why a tank full of water appears less deep than it actually is.
How does the light have to enter the glass:
for no refraction to happen?
The speed of light is more in glass than in water.
Image is formed by a mirror due to refraction of light.
Water is optically .......... than air.
Match the Following
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) white Light | (1) Convex mirror |
| (b) Refraction | (2) Concave mirror |
| (c) Virtual images | (3) refraction |
| (d) Real images | (4) spectrum |
| (e) Prism | (5) ray of light from glass to air |
A ray of light passes from medium 1 to medium 2. Which of the following quantities of the refracted ray will differ from that of the incident ray: Speed, intensity, frequency, wavelength?
A ray of light A incident from air suffers partial reflection and refraction at the boundary of water.
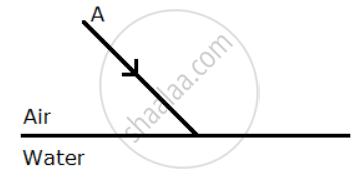
- Complete the diagram showing (i) the reflected ray B and (ii) the refracted ray C.
- How are the angles of incidence i and refraction r related?
Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
The size of image of an object by a convex lens of focal length 20 cm is observed to be reduced to `1/3` rd of its size . Find the distance of the object from the optical centre of the lens .
List in proper sequence the steps of the experiment for determining the approximate focal length of a given concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object.
Write scientific reason.
The bottom of a pond appears raised.
Explain with diagrams how refraction of incident light takes place from
- rarer to denser medium
- denser to rarer medium
- normal to the surface separating the two media.
You are given water, mustard oil, glycerine and kerosene. In which of these media a ray of light incident obliquely at same angle would bend the most?
Which object use the reflection of light?
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1. | r > 90 | a. | Light gazes at the surface of separation between the two modes. |
| 2. | r = 90 | b. | No refraction. |
| 3. | r < 90 | c. | Refracted ray away from the normal |
A ray of light starting from diamond is incident on the interface separating diamond and water. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show. the refraction of light in this case.
