Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are ______.
Options
Perpendicular to each other.
Non-parallel to each other.
Parallel to each other.
Intersecting each other.
Solution
In the refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are parallel to each other.
Explanation:
For refraction to happen the light ray will have to incident obliquely. If the light ray is incident on the glass slab at a zero angle of incidence the ray will travel without any change of direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which property of light makes a pencil cast a shadow when it is held in front of a light source?
State whether the following statement is true of false:
A student says that we can see an object because light from our eyes is reflected back by the object.
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror such that its angle of incidence is 30°. What angle does the reflected ray make with the mirror surface?
What is lateral inversion? Explain by giving a suitable example.
An extended object in the form of an arrow pointing upward has been placed in front of a plane mirror. Draw a labelled ray-diagram to show the formation of its image.
State and explain the laws of reflection of light at a plane surface (like a plane mirror), With the help of a labelled ray-diagram. Mark the angles of 'incidence' and 'reflection' clearly on the diagram. If the angle of reflection is 47.5°, what will be the angle of incidence?
Write all the capital letters of the alphabet which look the same in a plane mirror.
The angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence:
(a) always
(b) sometimes
(c) under special conditions
(d) never
The image of an object formed by a plane mirror is:
(a) virtual
(b) real
(c) diminished
(d) upside-down
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror PQ at an angle of incidence of 30°, is reflected from the plane mirror and then strikes a second plane mirror QR placed at right angles to the first mirror. The angle of reflection at the second mirror is ______.
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a rectangular glass block and emerges out into the air from the opposite face. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the completer path of this ray of light. Mark the two points where the refraction of light takes place. What can you say about the final direction of ray of light?
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain why a tank full of water appears less deep than it actually is.
With the help of a diagram, show how when light falls obliquely on the side of a rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray.
State two factors on which the lateral displacement of the emergent ray depends.
Light travelling from a denser medium to a rarer medium along a normal to the boundary:
(a) is refracted towards the normal
(b) is refracted away from the normal
(c) goes along the boundary
(d) is not refracted
A vertical ray of light strikes the horizontal surface of some water:
What is the angle of incidence?
The depth of a pond when seen from above appears to be less.
Light travels at a lower speed in water than in air.
Image is formed by a mirror due to refraction of light.
Air is optically .......... than glass.
When a ray of light travels from air to glass, it bends .......... the normal.
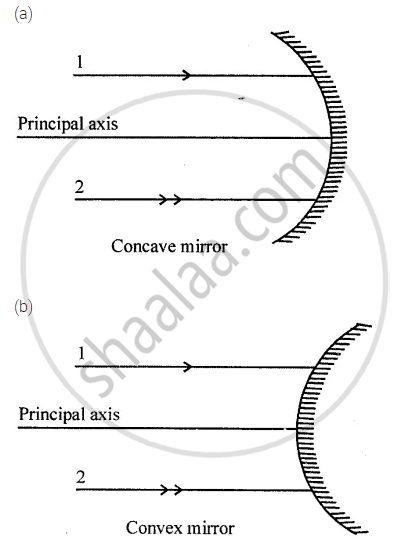
The diagram (figure) given below shows two parallel rays 1 and 2 incident on (a) a concave mirror, (b) a convex mirror. Draw the reflected rays and mark the focus by the symbol F.
A light ray suffers reflection and refraction at the boundary in passing from air to water. Draw a neat labelled ray diagram to show it.
Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 × 108 m s−1.
List in proper sequence the steps of the experiment for determining the approximate focal length of a given concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object.
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
Light changes its direction when going from one transparent medium to another transparent medium. This is called _______.
Write scientific reason.
A pencil appears to be broken near the surface of water.
Observe the given figure and write appropriate phenomenon of light in the box.

The deviation of light ray from its path when it travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium is called ______.

The angle of incidence from air to glass at the point O on the hemispherical glass slab is.
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of ______ is constant.
Assertion: The air bubble shines in water.
Reason: Air bubble shines due to the refraction of light.
How do twinkling stars occur? (or) what is the cause of the twinkling of stars?
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1. | r > 90 | a. | Light gazes at the surface of separation between the two modes. |
| 2. | r = 90 | b. | No refraction. |
| 3. | r < 90 | c. | Refracted ray away from the normal |
