Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In a right triangle ABC right-angled at C, P and Q are the points on the sides CA and CB respectively, which divide these sides in the ratio 2 : 1. Prove that
`(i) 9 AQ^2 = 9 AC^2 + 4 BC^2`
`(ii) 9 BP^2 = 9 BC^2 + 4 AC^2`
`(iii) 9 (AQ^2 + BP^2 ) = 13 AB^2`
उत्तर
It is given that P divides CA in the ratio 2 : 1. Therefore,
`CP=\frac { 2 }{ 3 }AC ….(i)`
Also, Q divides CB in the ratio 2 : 1.
`∴ QC=\frac { 2 }{ 3 }BC ….(ii)`
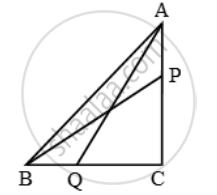
(i) Applying pythagoras theorem in right-angled triangle ACQ, we have
`AQ^2 = QC^2 + AC^2`
`⇒ AQ^2 = \frac { 4 }{ 9 } BC^2 + AC^2 `
`⇒ 9 AQ^2 = 4 BC^2 + 9 AC^2 ….(iii)`
(ii)Applying pythagoras theorem in right triangle BCP, we have
`BP^2 = BC^2 + CP^2`
`⇒ BP^2 = BC^2 + AC^2 `
`⇒ 9 BP^2 = 9 BC^2 + 4 AC^2 ….(iv)`
(iii)Adding (iii) and (iv), we get
`9 (AQ^2 + BP^2 ) = 13 (BC^2 + AC^2 )`
`⇒ 9 (AQ^2 + BP^2 ) = 13 AB^2 [∵ BC^2 = AC^2 + AB^2 ]`
