Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
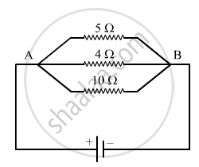
In the circuit diagram given below, the current flowing across 5 ohm resistor is 1 amp. Find the current flowing through the other two resistors.
उत्तर
Given I = 1 A (Across 5 Ω)
R = 5 Ω
The potential drop across AB, V = I x R
or V = 5 Ω x 1 A = 5 V
In a parallel circuit, the potential difference across the ends of all resistors remains the same. Therefore, the potential difference across 4 Ω and 10 Ω will be 5 V:
The current flowing through the 4 Ω resistor, I = V/R.
Here, V = 5 V
R = 4 Ω
So, I = 5/4 = 1.25 A
The current flowing through the 10 Ω resistor, I = V/R.
Here, V = 5 V
R = 10 Ω
So. I = 5/10 = 0.5 A
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State two causes of energy loss in a transformer.
What do the letters p.d. stand for?
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become:
If the potential difference between the end of a wire of fixed resistance is doubled, by how much does the electric power increase?
Electric cells having 2V potential difference each have been connected in the form of a battery. What will be the total potential difference of the battery in both cases?
Define the following:
Potential difference
A 10 m long wire of a particular material is of resistance 5Ω What will be the resistance if the wire is doubled itself.
Potential near a charge is the measure of its ______ to bring a positive charge at that point.
A boy records that 4000 joules of work are required to transfer 10 coulombs of charge between two points of a resistor of 50 Ω. The current passing through it is: