Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In the figure, given that ∠1 = ∠2 and ∠3 ≡ ∠4. Prove that ∆MUG ≡ ∆TUB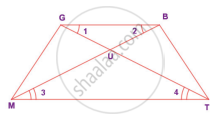
उत्तर
| Statements | Reasons |
|
1. In ΔMUG and ΔTUG MU = TU |
∠3 = ∠4, opposite sides of equal angles |
| 2. UG = UB |
∠1 = ∠2 Side opposite to equal angles are equal |
| 3. ∠GUM = ∠BUT | Vertically opposite angle |
| 4. ∆MUG ≡ ∆TUG |
SAS criteria By 1, 2 and 3 |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In the given figure, ΔBCD is isosceles with base BD and ∠BAE ≡∠DEA. Prove that AB ≡ ED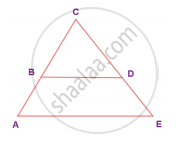
To conclude the congruency of triangles, mark the required information in the following figure with reference to the given congruency criterion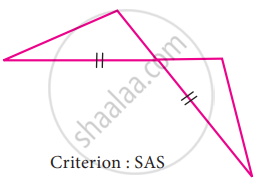
For the given pair of triangles state the criterion that can be used to determine the congruency?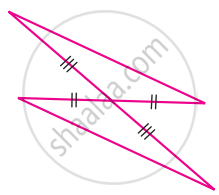
Construct a triangle ABC with given conditions.
AB = 7 cm, AC = 6.5 cm and ∠A = 120°
Construct a triangle XYZ with the given conditions.
BC = 8 cm, AC = 6 cm and ∠C = 40°
Using the given figure, prove that the triangles are congruent. Can you conclude that AC is parallel to DE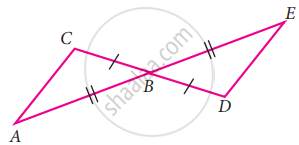
In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.

In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.
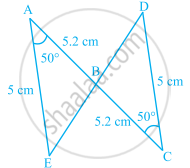
In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.
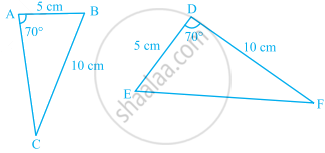
In the given figure, which pairs of triangles are congruent by SAS congruence criterion (condition)? if congruent, write the congruence of the two triangles in symbolic form.

