Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Indian style of cooling drinking water is to keep it in a pitcher having porous walls. Water comes to the outer surface very slowly and evaporates. Most of energy needed for evaporation is taken from the water itself and the water is cooled down. Assume that a pitcher contains 10 kg of water and 0.2 g of water comes out per second. Assuming no backward heat transfer from the atmosphere to the water, calculate the time in which the temperature decrease by 5°C. Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1 and latent heat of vaporization of water = 2.27 × 106 J kg−1.
उत्तर
Given:-
Specific heat of water ,S = 4200 J kg−1 °C−1
Latent heat of vapourisation of water ,L = 2.27 × 106 J kg−1
Mass, M = 0.2 g = 0.0002 kg
Let us first calculate the amount of energy required to decrease the temperature of 10 kg of water by 5°C.
U1 = 10 × 4200 J/kg°C × 5°C
U1 = 210,000 = 21 × 104 J
Let the time in which the temperature is decreased by 5°C be t.
Energy required per second for evaporation of water (at the rate of 0.2 g/sec) is given by
U2 = ML
U2 = (2 × 10−4 )× (2.27 × 106) = 454 J
Total energy required to decrease the temperature of the water = 454 × t
= 21 × 104 J
Now,
\[t= \frac{21 \times {10}^4}{454}\text{ seconds}\]
The time taken in minutes is given by
\[t= \frac{21 \times {10}^4}{454 \times 60} = 7 . 7\text{ minutes}\]
∴ The time required to decrease the temperature by 5°C is 7.7 minutes.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What do you understand by the following statements:
The specific heat capacity of lead is 130 Jkg-1K-1.
State two factors upon which the heat absorbed by a body depends
During the phase change does the average kinetic energy of the molecules of the substance increase?
Water is used in hot water bottles for fomentation. Give a reason.
An electric heater of power 600 W raises the temperature of 4.0 kg of a liquid from 10.0℃ to 15.0℃ in100 s. Calculate:
- the heat capacity of 4.0 kg of liquid,
- the specific heat capacity of the liquid.
What is carbon tax?
Without green house effect, the average temperature of earth’s surface would have been:
(a) – 18℃
(b) 33℃
(c) 0℃
(d) 15℃
What is meant by specific heat capacity?
How will you prove experimentally that different substances have different specific heat capacities?
Solve the following problems:
Equal heat is given to two objects A and B of mass 1 g. Temperature of A increases by 3°C and B by 5°C. Which object has more specific heat? And by what factor?
Study the following procedure and answer the questions below:
1. Take 3 spheres of iron, copper and lead of equal mass.
2. Put all the 3 spheres in boiling water in a beaker for some time.
3. Take 3 spheres out of the water. Put them immediately on a thick slab of wax.
4. Note, the depth that each sphere goes into the wax.
i) Which property of substance can be studied with this procedure?
ii) Describe that property in minimum words.
iii) Explain the rule of heat exchange with this property.
The ratio of specific heat capacity to molar heat capacity of a body _____________ .
(b) 2000 J of heat energy is required to raise the temperature of 4 kg of a
metal by 3°c. Which expression gives the specific heat capacity of the metal?
650 J of heat is required to raise the temp. of 0.25 kg of lead from 15°C to 35°C. Calculate the Sp. heat capacity of lead.
Specific heat capacity of a substance A is 3.8 J g-1 K-1 and of substance B is 0.4 J g-1 k-1. Which substance is a good conductor of heat? How did you arrive at your conclusion?
A liquid X has specific heat capacity higher than the liquid Y. Which liquid is useful as heat reservoir to keep juice bottles without freezing?
A piece of iron of mass 2.0 kg has a heat capacity of 966 J K-1. Find its specific heat capacity in S.I unit.
Water boils at 120 °C in a pressure cooker. Explain the reason
What are the factors on which the quantity of heat given to a body depends?
Does the specific heat capacity of a substance depend upon its mass and rise in temperature only?
Write the approximate values of the specific latent heat of fusion of ice.
The farmers fill their fields with water in winter. Give reason.
The temperature of a lead piece of mass 400 g rises from 20°C to 50°C when 1560 J of heat is supplied to it. Calculate Specific heat capacity of lead.
A. hot solid of mass 60 g at 100°C is placed in 150 g of water at 20° C. The final steady temperature recorded is 25°C. Calculate the specific heat capacity of the solid. [Specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg-1 °C-1]
A piece of iron of mass 2.0 kg has a thermal capacity of 966 J/°C. What is its specific heat capacity in S.I. units?
Solve the following problem.
Specific latent heat of vaporization of water is 2.26 × 106 J/kg. Calculate the energy needed to change 5.0 g of water into steam at 100 ºC.
State factors on which the amount of heat radiated by a body depends.
How much heat energy is necessary to raise the temperature of 5 kg of water from 20°C to 100°C?
The specific heat capacity of water is 1 cal/g °C.
Read this activity and answer the following questions.
- Take three spheres of iron, copper and lead. the lead of equal mass.
- Put all the three spheres in boiling water in the beaker for some time.
- Take the three spheres out of the water.
- All the spheres will be at a temperature 100 °C.
- Put them immediately on the thick slab of wax.
- Note, the depth that each of the sphere goes into the wax.
Questions:
- Which property is determined from this activity?
- Give name to that property.
- Explain the term principal of heat exchange with the help of this activity.
Express the change in internal energy in terms of molar specific heat capacity.
A monoatomic gas of pressure 'P' having volume 'V' expands isothermally to a volume '2V' and then adiabatically to a volume '16V'. The final pressure of the gas is ______.
(ratio of specific heats = `5/3`)
If 'f' is the number of degrees of freedom of a molecule of a gas and ratio of molar specific heats of a gas, ϒ = 1 + `2/"f"` where ϒ = Cp/Cv. The ratio of 'ϒ' for monoatomic gas to 'ϒ' for (rigid) f diatomic gas is ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for 200 g of water. The heat is extracted at the rate of 100 Js-1. Answer the questions that follow:
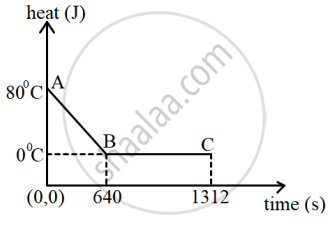
- Calculate specific heat capacity of water.
- Heat released in the region BC.
A geyser heats water flowing at a rate of 2.0 kg per minute from 30°C to 70°C. If the geyser operates on a gas burner, the rate of combustion of fuel will be ______ g min-1.
[Heat of combustion = 8 × 103 Jg-1 Specific heat of water = 4.2 Jg-1°C-1]
The molar specific heats of an ideal gas at constant pressure and volume are denoted by Cp and Cv, respectively. If `gamma = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v"` and R is the universal gas constant, then Cv is equal to ______.
