Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Joseph jogs from one end A to the other end B of a straight 300 m road in 2 minutes 30 seconds and then turns around and jogs 100 m back to point C in another 1 minute. What are Joseph’s average speeds and velocities in jogging?
- from A to B and
- from A to C?
उत्तर
(a) From A to B.

Time for A to B = 2 min 30s
= 2 × 60 + 30
= 150 s
`"Average speed" = "total distance"/ "time interval"`
= `300/150`
= 2 ms-1
`"Average velocity" = "displacement"/ "time interval"`
= `300/150`
= 2 ms-1
(b) From A to C.
Time taken = A to B + B to C
= 150 + 60
= 210 s
Total distance = 300 + 100
= 400 m
∴ `"Average speed" = "total distace"/"time interval"`
= `400/210 `
= 1.9 m s-1
∴ `"Average velocity" = "displacement"/"time interval"`
= `200/210`
= 0.95 ms-1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Under what condition(s) is the magnitude of average velocity of an object equal to its average speed?
State whether speed is a scalar or a vector quantity. Give reason for your choice.
If a bus travelling at 20 m/s is subjected to a steady deceleration of 5 m/s2, how long will it take to come to rest ?
A car is moving along a straight road at a steady speed. It travels 150 m in 5 seconds:
How far does it travel in 6 seconds ?
A ball hits a wall horizontally at 6.0 m s-1. It rebounds horizontally at 4.4 m s-1. The ball is in contact with the wall for 0.040 s. What is the acceleration of the ball ?
Which of the following can sometimes be 'zero' for a moving body?
(i) average velocity
(ii) distance travelled
(iii) average speed
(iv) displacement
Give an example of the motion of a body moving with a constant speed but with a variable velocity. Draw a diagram to represent such a motion.
Arrange the following speeds in increasing order.
10 m s-1, 1 km min-1 and 18 km h-1.
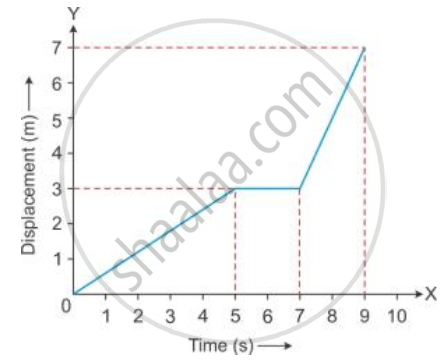
Figure shows the displacement of a body at different times .
Calculate the velocity of the body as it moves for time interval :
(i) 0 to 5 s,
(ii) 5 s to 7 s
(iii) 7 s to 9 s.
Define uniform velocity and give one example.
