Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. By how much does the current change?
उत्तर
We know that V = IR
If V is constant, resistance is doubled R' = 2R.
Then V' = I'R'
V' = V since V is constant`
` V=Txx2xxR`
`T=(v)/(2R)=I/2`
Thus, the current will get reduced to half.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How much energy is transferred by a 12 V Power supply to each coulomb of charge which it moves around a circuit?
The device used for measuring potential difference is known as:
The other name of potential difference is:
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is halved. By how much does the current change?
The values of potential difference V applies across a resistor and the corresponding values of current I flowing in the resistor are given below:
| Potential differences, V (in volts) | : | 2.5 | 5.0 | 10.0 | 15.0 | 20.0 | 25.0 |
| Current, I (in amperes) | : | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
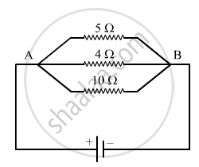
In the circuit diagram given below, the current flowing across 5 ohm resistor is 1 amp. Find the current flowing through the other two resistors.
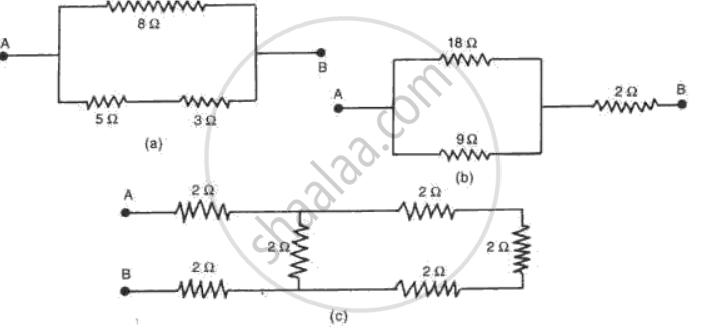
What is the combined resistance of each of the networks between A and B shown in fig. ?
A cell of e.m.f 2.0 V and internal resistance 1Ω is connected to the resistors of 3Ω and 6Ω in series. Calculate:
(i) the current drawn from the cell,
(ii) the p.d. across each resistor,
(iii) the terminal voltage of the cell and
(iv) the voltage drop.
State Ohm’s law.
Define electric potential and potential difference.
