Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match materials given in Column I with the polymers given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Natural rubber latex | (a) Nylon |
| (ii) Wood laminates | (b) Neoprene |
| (iii) Ropes and fibres | (c) Dacron |
| (iv) Polyester fabric | (d) Melamine formaldehyde resins |
| (v) Synthetic rubber | (e) Urea-formaldehyde resins |
| (vi) Unbreakable crockery | (f) cis-polyisoprene |
उत्तर
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Natural rubber latex | (f) cis-polyisoprene |
| (ii) Wood laminates | (e) Urea-formaldehyde resins |
| (iii) Ropes and fibres | (a) Nylon |
| (iv) Polyester fabric | (c) Dacron |
| (v) Synthetic rubber | (b) Neoprene |
| (vi) Unbreakable crockery | (d) Melamine formaldehyde resins |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write names and chemical formulae of monomers used in preparing Buna-S.
How does the presence of double bonds in rubber molecules influence their structure and reactivity?
Discuss the main purpose of vulcanisation of rubber.
Write the structures of monomers used the following polymers:
Buna S
Which of the following are example of synthetic rubber?
(i) Polychloroprene
(ii) Polyacrylonitrile
(iii) Buna-N
(iv) cis-polyisoprene
Vulcanisation makes rubber:
(i) more elastic
(ii) soluble in inorganic solvent
(iii) crystalline
(iv) more stiff
Identify the polymer given below:
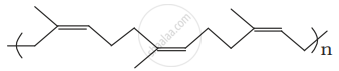
Which one of the following monomers gives the polymer neoprene on polymerization?
Which of the following is correct regarding the drawbacks of raw rubber.
Which of the following statement is CORRECT regarding the drawbacks of raw rubber?
