Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Match the following
| I) | External fertilization | i) | pollen grain |
| II) | Androecium | ii) | anther wall |
|
III) |
Male gametophyte | iii) | algae |
| IV) | Primary parietal layer | iv) | stamens |
विकल्प
I-iv;II-i;III-ii;IV-iii
I-iii;II-iv;III-i;IV-ii
I-iii;II-iv;III-ii,IV-i
I-iii;II-i;III-iv;IV-ii
उत्तर
I-iii;II-iv;III-ii,IV-i
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is double fertilisation? Describe the process in brief.
Explain the Following Term:
Ornithophily
Explain the following term:
Elephophily
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
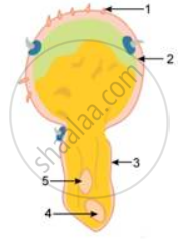
Where does the germination of the pollen grain take place and how?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:

What part does the stigma play in the process of fertilisation?
What is ‘double fertilization’? Describe it with the help of a neat and well-labeled diagram. Give its importance.
What is ‘double fertilization’? Describe it with the help of a neat and well-labeled diagram. Give its importance.
What is the function of pollen tube? Explain with the help of a diagram.
What happens to the ovary post fertilization?
The seed is a fertilized _______.
Which of the following represent megagametophyte
What is polyembryony? How it can commercially exploited.
Identify the function of filiform apparatus.
From the following identify the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid.
If the cells of the nucellus in the angiosperm ovule contain 24 chromosomes, then ____________ chromosomes will be present in the endosperm of a self-pollinated flower.
Fusion of one of the male gametes with egg nucleus is referred to as ______.
Double fertilization is a distinctive feature of ______.
All the events from pollen deposition on the stigma until pollen tubes enter the ovules are together referred to as ______.
Identity the part of embryo sac which takes part in formation of primary endosperm nucleus during fertlisation
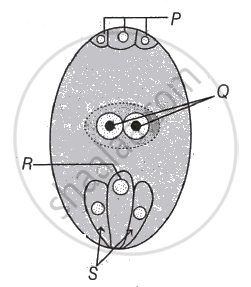
What is Siphonogamy?
