Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Match the following
| I) | External fertilization | i) | pollen grain |
| II) | Androecium | ii) | anther wall |
|
III) |
Male gametophyte | iii) | algae |
| IV) | Primary parietal layer | iv) | stamens |
Options
I-iv;II-i;III-ii;IV-iii
I-iii;II-iv;III-i;IV-ii
I-iii;II-iv;III-ii,IV-i
I-iii;II-i;III-iv;IV-ii
Solution
I-iii;II-iv;III-ii,IV-i
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
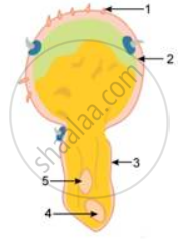
Where does the germination of the pollen grain take place and how?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
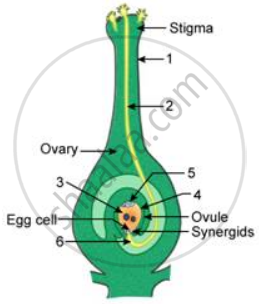
Name the parts labelled 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6.
Even though each pollen grain has 2 male gametes, why at least 20 pollen grains are required to fertilize 20 ovules in a particular carpel?
Describe the process of double fertilization.
Long Answer Question:
Draw a labeled diagram of the L.S. of anatropous ovule and list the components of the embryo sac and mention their fate after fertilization.
Give any four points of significance of double fertilization.
Describe the process of double fertilization in angiosperms and add a note on its significance.
After fertilization the ovule becomes ______.
Syngamy results in the formation of ______.
Transmitting tissue is found in
In majority of plants pollen is liberated at
What is Mellitophily?
‘Pollination in Gymnosperms is different from Angiosperms’ – Give reasons.
In double fertilization, the first male gamete fuses with the egg and the second male gan1ete fuses with which of the following?
In angiosperms, for formation of which of the following triple fusion is necessary?
Fusion of one of the male gametes with egg nucleus is referred to as ______.
In ______ sepal is seen on the fruit after fertilization.
What is the function of the two male gametes produced by each pollen grain in angiosperms?
Give a term for the following:
Fusion of male gamete and secondary nucleus in angiosperms.
