Advertisements
Advertisements
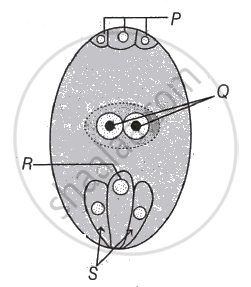
Question
In majority of plants pollen is liberated at
Options
1 celled stage
2 celled stage
3 celled stage
4 celled stage
Solution
2 celled stage
RELATED QUESTIONS
Read the following statement and answer the questions that follow :
"A guava fruit has 200 viable seeds."
(a) What are viable seeds?
(b) Write the total number of :
(i) Pollen grains (ii) Gametes
in producing 200 viable guava seeds.
c) Prepare a flow-chart to depict the post-pollination events leading to viable-seed production in a flowering plant.
(a) Explain the events after pollination leading to the formation of a seed in angiosperms.
(b) Mention the ploidy levels of the cells of different parts of an albuminous seed.
What happens to the following after fertilization?
Petals
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
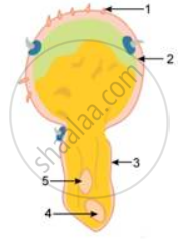
Where does the germination of the pollen grain take place and how?
Expand the following abbreviation IW.
Explain the pollination process in Salvia
What is a fruit?
Do you think fruits are important for the plant?
Even though each pollen grain has 2 male gametes, why at least 20 pollen grains are required to fertilize 20 ovules in a particular carpel?
Describe the process of double fertilization in angiosperms and add a note on its significance.
After fertilization the ovule becomes ______.
Size of pollen grain in Myosotis
Syngamy results in the formation of ______.
Double fertilization and triple fusion were discovered by ______.
The female gametophyte of a typical dicot at the time of fertilisation is ______.
The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilisation in angiospersm are ______.
After fertilization, the seed coat of seeds develops from ______
Can an unfertilised, apomictic embryo sac give rise to a diploid embryo? If yes, then how?
Which is the triploid tissue in a fertilised ovule? How is the triploid condition achieved?
Identity the part of embryo sac which takes part in formation of primary endosperm nucleus during fertlisation