Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Name a disorder a human suffers from as a result of the monosomy of the sex chromosome. Give the karyotype and write the symptoms.
उत्तर
Turner's Syndrome is a result of the monosomy of the sex chromosome in humans.
Its karyotype is XO i.e. 45 chromosomes.
Symptoms -
- short stature
- lack of the development of the ovaries
- lack of secondary sexual characteristics
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
(a) Why are thalassemia and haemophilia categorized as Mendelian disorders? Write the symptoms of these diseases. Explain their pattern of inheritance in humans.
(b) Write the genotypes of the normal parents producing a haemophilic son.
Given below is the representation of amino acid composition not the relevant translated portion of β-chain of haemoglobin, related to the shape of human red blood cells
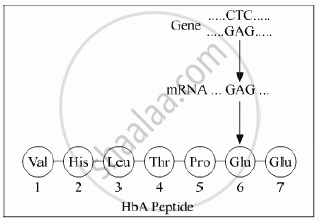
(a) Is this representation indicating a normal human or a sufferer from certain related genetic disease? Give reason in support of your answer.
(b) What difference would be noticed in the phenotype of the normal and the sufferer related to this gene?
(c) Who are likely to suffer more from the defect related to the gene represented the males, the females or both males and females equally? And why?
A couple with normal vision bear a colour blind child. Work out a cross to show how it is possible and mention the sex of the affected child.
Match the column-I with column-II and re-write the matching pairs.
| Column-I | Column-II |
| 1. 21 trisomy | a. Turner’s syndrome |
| 2. X-monosomy | b. Klinefelter’s syndrome |
| 3. Holandric traits | c. Down's syndrome |
| 4. Feminized male | d. Hypertrichosis |
What is the reason for the 21st trisomy?
Identify the disease caused by an autosomal primary non-disjunction.
Thalassemia and sickle cell anemia are caused due to a problem in globin molecule synthesis. Select the correct statement.
It is well known that Queen Victoria of England was a carrier for haemophilia. Since this is an X-linked disease, it can be predicted that ______.
The most striking example of point mutation is found in a disease called ______.
Read the following and answer from given below:
Turner's syndrome is an example of monosomy. It is formed by the union of an allosome-free egg and a normal 'X' containing sperm or a normal egg and an allosome-free sperm. The individual has 2n = 45 chromosomes (44 + X0) instead of 46. Such individuals are sterile females who have rudimentary ovaries, underdeveloped breasts, small uterus, short stature, webbed neck, and abnormal intelligence. They may not menstruate or ovulate. This disorder can be treated by giving female sex hormones to women from the age of puberty to make them develop breasts and have menstruation. This makes them feel more normal.
The number of Barr bodies present in a female with Turner's syndrome is ______
