Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Obtain the macroscopic form of Ohm’s law from its microscopic form and discuss its limitation.
उत्तर
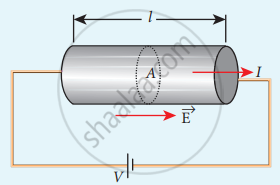
- Consider a segment of wire of length l and area of cross-section A
- Electric field is created when a potential difference V is applied
- If ‘E’ is uniform, then, V = El
- Current density, J = σ E = σ`"V"/l`
Since J = `"I"/"A"`
`"I"/"A" = sigma "V"/l`
Rearranging the above equation, Current through the conductor
Current through the conductor
V = `"I"(l/(sigma"A"))`
Where `(l/(sigma"A"))` → resistance of conductor (R)
∴ R `alpha (l/(sigma"A"))`
∴ The macroscopic form of Ohm's law is
V = IR ...[V α I]
Limitations:
There are certain materials and devices where the proportionality of V and I does not hold good.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material Ga As is shown in the figure. Identify the region of
(i) negative resistance
(ii) where Ohm's law is obeyed.
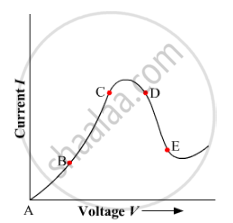
Name the law which is illustrated by the above V−I graph.
How would you connect two resistors in series? Draw a diagram. Calculate the total equivalent resistance.
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 Ω. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
What are non-ohmic conductors? Give one exmaple. Draw a current-voltage graph for a non-ohmic conductor.
An ammeter placed in series with an electric radiator reads 0.5 amps and a voltmeter placed across it reads 230 volts. What is the resistance of the radiator?
Ohm’s law states the relationship between power and voltage.
The slope of voltage (V) versus current (I) is called:
You are provided with a resistor, a key, an ammeter, a voltmeter, four cells of 1.5 V each and few connecting wires. Using circuit components, draw a labelled circuit diagram to show the setup to study Ohm's law.
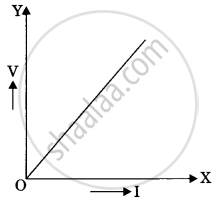
State the relationship between potential difference (V) across the resistor and the current (I) flowing through it. Also draw V-I graph, taking V on the X-axis.
The resistance of a resistor is reduced to half of its initial value. If other parameters of the electrical circuit remain unaltered, the amount of heat produced in the resistor will become ______.
