Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Explain the equivalent resistance of a series resistor network.
उत्तर
When two or more resistors are connected end to end, they are said to be in series. The resistors could be simple resistors or bulbs or heating elements or other devices. Fig. (a) shows three resistors R1, R2 and R3 connected in series.

Three resistors in series
The amount of charge passing through resistor R1 must also pass through resistors R2 and R3 since the charges cannot accumulate anywhere in the circuit. Due to this reason, the current I passing through all the three resistors is the same. According to Ohm’s law, if same current pass through different resistors of different values, then the potential difference across each resistor must be different. Let V1, V2 and V3 be the potential difference (voltage) across each of the resistors R1, R2 and R3 respectively, then we can write V1 = IR1, V2 = IR2 and V3= IR3. But the total voltage V is equal to the sum of voltages across each resistor.
V = V1 + V2 + V3
= IR1 + IR2 + IR3 ….. (1)
V = I(R1 + R2 +R3)
V = I.RS …… (2)
where Rs = R1 + R2 R3 ……. (3)
When several resistances are connected in series, the total or equivalent resistance is the sum of the individual resistances as shown in the following figure.
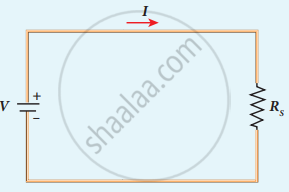
Equivalent resistance (RS) has the same current
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What will be the change in the current if the potential difference is kept constant and the resistance of the circuit is made four times?
- It will remain unchanged.
- It will become four times.
- It will become one-fourth.
- It will become half.
Find the resistance of a conductor if 0.24 A current is passing through it and a potential difference of 24 V is applied across it.
Write the SI unit of resistivity
The graph between V and I for a conductor is a straight line passing through the origin.
What should remain constant in a statement of this law?
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of Ohm's law. Label the parts from A to F. state the function of each.
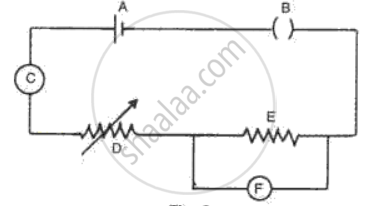
- Name and state the law which relates the potential difference and current in a conductor.
- What is the necessary condition for a conductor to obey the law named above in part (a) ?
State and define Ohm’s law.
Define Current density.
The voltage - current readings of a certain material are shown in the table given below:
| Voltage (V) | 10 V | 20 V | 30 V |
| Current (I) | 2 A | 3 A | 4 A |
Study the table.
- State whether the conductor used is ohmic or non-ohmic.
- Justify your answer.
- State Ohm's law.
