Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
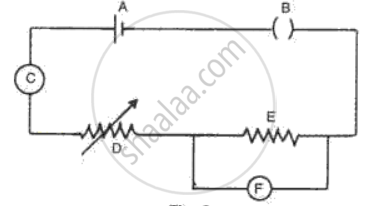
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of Ohm's law. Label the parts from A to F. state the function of each.
उत्तर
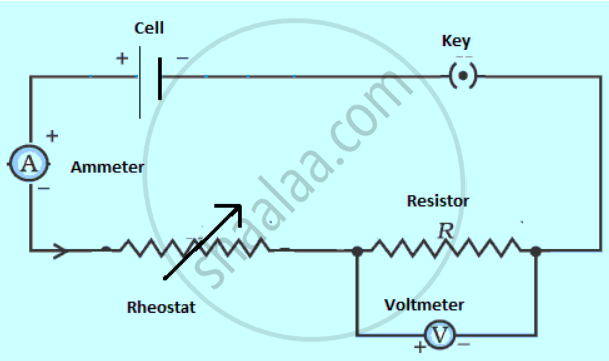
Functions:
(A) Cell- It provides the potential difference in the circuit.
(B) Key- It serves as a switch in the circuit. It supplies or cuts off current as required.
(C) Ammeter- It measures the current in the circuit.
(D) Rheostat- It helps to change the resistance of the circuit without changing its voltage.
(E) Resistor- It provides a constant resistance in the circuit.
(F) Voltmeter- It measure the potential drop across the resistor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is an Ohmic resistor?
When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Calculate the value of the resistance of the resistor.
State Ohm’s law and draw a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a rheostat and an unknown resistance to verify it.
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 Ω. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
The filament of a bulb takes a current 100 mA when potential difference across it is 0.2 V. When the potential difference across it becomes 1.0 V, the current becomes 400 mA. Calculate the resistance of filament in each case and account for the difference.
Define ampere and volt with respect to Ohm’s law.
Define Current density.
State Ohm’s law? How can it be verified experimentally? Does it hold good under all conditions? Comment.
Let the resistance of an electrical device remain constant, while the potential difference across its two ends decreases to one fourth of its initial value. What change will occur in the current through it? State the law which helps us in solving the above stated question.
