Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The filament of a bulb takes a current 100 mA when potential difference across it is 0.2 V. When the potential difference across it becomes 1.0 V, the current becomes 400 mA. Calculate the resistance of filament in each case and account for the difference.
उत्तर
According to Ohm's law,
V = IR
∴ R = `"V"/"I"`
`therefore "R"_1 = "V"_1/"I"_1`
= `0.2/0.1 = 2 Omega`
Similarly ,
`"R"_2 = "V"_2/"I"_2`
= `1/0.4`
= 2.5 Ω
Resistance of the wire increases with increase in temperature. So the difference arises because the temperature of the filament increased.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Is Ohm’s law universally applicable for all conducting elements? If not, give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm’s law.
What is an Ohmic resistor?
Name the law which is illustrated by the above V−I graph.
A car bulb connected to a 12 volt battery draws 2 A current when glowing. What is the resistance of the filament of the bulb? Will the resistance be more same or less when the bulb is not glowing?
In an experiment of verification of Ohm’s law following observations are obtained.
|
Potential difference V (in volt) |
0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| current I (in ampere) | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 |
Draw a V-I graph and use this graph to find:
- the potential difference V when the current I is 0.5 A,
- the current I when the potential difference V is 0.75 V,
- the resistance in a circuit.
A wire of resistance 3 ohm and length 10 cm is stretched to length 30 cm. Assuming that it has a uniform cross section, what will be its new resistance?
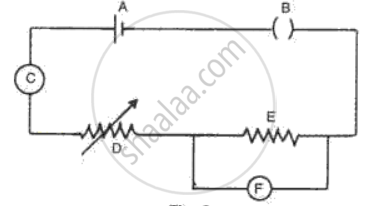
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of Ohm's law. Label the parts from A to F. state the function of each.
State macroscopic form of Ohm’s law.
The temperature of a conductor is increased. The graph best showing the variation of its resistance is:
A current of 0.8 A flows in a conductor of 40 Ω for 1 minute. The heat produced in the conductor will be ______.
