Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
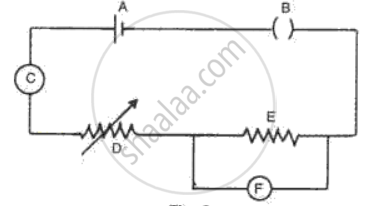
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of Ohm's law. Label the parts from A to F. state the function of each.
Solution
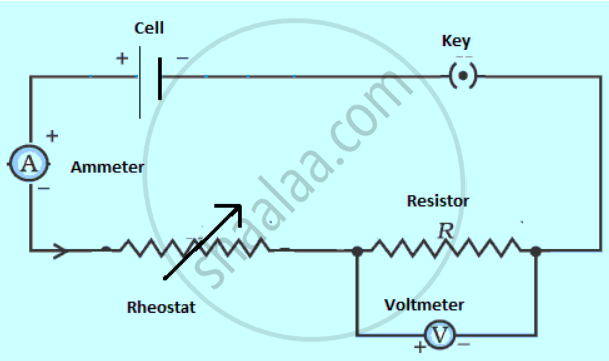
Functions:
(A) Cell- It provides the potential difference in the circuit.
(B) Key- It serves as a switch in the circuit. It supplies or cuts off current as required.
(C) Ammeter- It measures the current in the circuit.
(D) Rheostat- It helps to change the resistance of the circuit without changing its voltage.
(E) Resistor- It provides a constant resistance in the circuit.
(F) Voltmeter- It measure the potential drop across the resistor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Is Ohm’s law universally applicable for all conducting elements? If not, give examples of elements which do not obey Ohm’s law.
What is an Ohmic resistor?
Name the physical quantity whose unit is "ohm".
Ohm's law gives a relationship between:
(a) current and resistance
(b) resistance and potential difference
(c) potential difference and electric charge
(d) current and potential difference
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of ohm's law. Label the different parts from A and F. State the function of each.
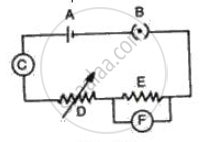
- Name and state the law which relates the potential difference and current in a conductor.
- What is the necessary condition for a conductor to obey the law named above in part (a) ?
What is meant by the drift speed of free electrons?
What is non-ohmic resistor?
Obtain the macroscopic form of Ohm’s law from its microscopic form and discuss its limitation.
Let the resistance of an electrical device remain constant, while the potential difference across its two ends decreases to one fourth of its initial value. What change will occur in the current through it? State the law which helps us in solving the above stated question.
