Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
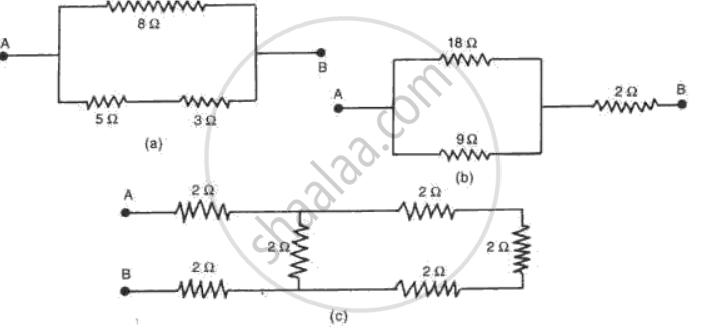
What is the combined resistance of each of the networks between A and B shown in fig. ?
Solution
(a) Between A andB,resistances 5Ω and 3 Ω are connected in series
·. Rs =5+3=8Ω
This series combination of resistances 5Ω and 3Ω is connected in parallel with the resistance 80
:. total resistance between A and Bis given as:
R = `[1/8 + 1/8]^-1` = 4Ω
(b) Bet ween A and B ,paralle combination of resistances 9Ω and 18Ω is connected in series with resistance 2Ω.
Parallel resistance of 9Ω and 18Ω is :
Rp = `[1/9 + 1/18]^-1` = 6Ω
:. total resistance between A and B is:
R=6+2=8Ω
(c) The situation consists of three two ohm resistors connected in series between CEFD and their combination in parallel with the fourth 2 ohm resistor between C and D.
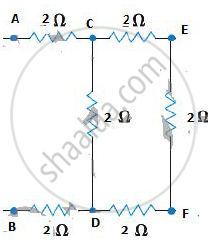
Therefore, series combination gives, 2 + 2 + 2 = 6 Ω.
This 6Ω resistor is connected in para lie I to the fourth 2Ω n resistor, therefore equivalent resistance between C and D,
`1/"R" = 1/6 + 1/2 = 2/3 Ω`
.·.R=l.5Ω
Now, between A and B the resistance Rand two 2Ω resistors are connected in series.
Therefore, equivalent resistance between A and B is
Rtotal = 2+2 +1.5 =5.5 Ω
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
What is the SI unit of potential difference?
Potential difference is measured in _________ by using a ___________ placed in ___________ across a component.
Keeping the potential difference constant, the resistance of a circuit is doubled. The current will become:
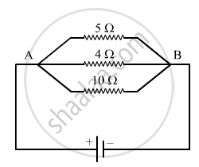
In the circuit diagram given below, the current flowing across 5 ohm resistor is 1 amp. Find the current flowing through the other two resistors.
State the S.I. unit of electric potential.
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
Which law will the graph prove? Explain the law.

Five resistors of different resistances are connected together as shown in the figure. A 12 V battery is connected to the arrangement.

Calculate:
(i) the total resistance in the circuit
(ii) the total current flowing in the circuit.
Assertion (A): Charges flow from higher potential to lower potential.
Reason (R): Current flows mainly due to the flow of electrons.
Define Electric potential.
