Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Find the resistance of a conductor if 0.24 A current is passing through it and a potential difference of 24 V is applied across it.
उत्तर
Data :I = 0.24 A, V= 24 V
To find: R = ?
Solution: V = IR
R = V/I
R = 24/0.24
R = 100 Ω
The resistance of the conductor is 100 Ω.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the potential difference across the ends of a conductor is 220 V and the resistance of the conductor is 44 Ω (ohm), then the current flowing through is _________.
- 0.2 A
- 0.5 A
- 2 A
- 5 A
What will be the change in the current if the potential difference is kept constant and the resistance of the circuit is made four times?
- It will remain unchanged.
- It will become four times.
- It will become one-fourth.
- It will become half.
What is Resistivity?
An electrical bulb is marked 200V, 100W. Calculate the electrical resistance of its filament. If five such
bulbs are connected in series to a 200V supply, how much current will flow through them?
Name the law which is illustrated by the above V−I graph.
How should the two resistances of 2 ohms each be connected so as to produce an equivalent resistance of 1 ohm?
How much energy is consumed when a current of 5 amperes flows through the filament (or element) of a heater having resistance of 100 ohms for two hours? Express it in joules.
State Ohm’s law and draw a neat labelled circuit diagram containing a battery, a key, a voltmeter, an ammeter, a rheostat and an unknown resistance to verify it.
Which of the following is an ohmic resistance?
In a conductor 6.25 × `10^16` electrons flow from its end A to B in 2 s. Find the current flowing through the conductor (e = 1.6 × `10^-19` C)
Calculate the current flowing through a wire of resistance 5 Ω connected to a battery of potential difference 3 V.
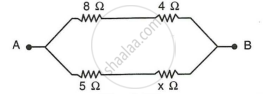
In the circuit shown below in Fig, calculate the value of x if the equivalent resistance between A and B is 4 Ω.
Calculate the electric field in a copper wire of cross-sectional area 2.0 mm2 carrying a current of 1 A.
The resistivity of copper = 1.7 × 10–8 Ω m
A metal sphere is kept on an insulting stands. A negatively charged rod is brought near it, then the sphere is earthed as shown. On removing the earthing, and taking the negatively charged rod away, what will be the nature of charge on the sphere? Give reason for your answer.
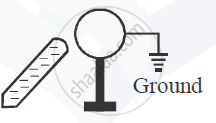
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of ohm's law. Label the different parts from A and F. State the function of each.
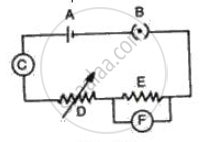
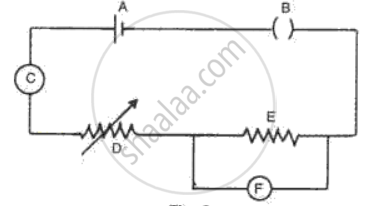
Fig. represents the circuit used for the verification of Ohm's law. Label the parts from A to F. state the function of each.
What are non-ohmic conductors? Give one exmaple. Draw a current-voltage graph for a non-ohmic conductor.
Choose the correct alternative.
Which of the following is an ohmic conductor?
A wire connected to a power supply of 230 V has power dissipation P1. Suppose the wire is cut into two equal pieces and connected parallel to the same power supply. In this case, power dissipation is P2. The ratio of `"P"_2/"P"_1` is
Define Current density.
State macroscopic form of Ohm’s law.
What is ohmic device?
Write a short note on superconductors?
Which of the following I-V graph represents ohmic conductors?
Which of the following is correct for V-I graph of a good conductor?
The temperature of a conductor is increased. The graph best showing the variation of its resistance is:
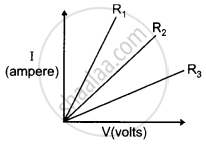
A student carries out an experiment and plots the V-I graph of three samples of nichrome wire with resistances R1, R2 and R3 respectively. Which of the following is hue?
Assertion: The statement of Ohm’s law is K = IR.
Reason: V = IR is the equation which defines resistance.
State Ohm’s law? How can it be verified experimentally? Does it hold good under all conditions? Comment.
The heat produced by a 100 w heater in 2 minute is equal to
A metal rod of length 10 cm and a rectangular cross-section of 1 cm × `1/2` cm is connected to a battery across opposite faces. The resistance will be ______.
Suppose there is a circuit consisting of only resistances and batteries and we have to double (or increase it to n-times) all voltages and all resistances. Show that currents are unaltered. Do this for circuit of Example 3.7 in the NCERT Text Book for Class XII.
How is electric current related to the potential difference across the terminals of a conductor?
Draw a labelled circuit diagram to verify this relationship.
A current of 0.8 A flows in a conductor of 40 Ω for 1 minute. The heat produced in the conductor will be ______.
The voltage - current readings of a certain material are shown in the table given below:
| Voltage (V) | 10 V | 20 V | 30 V |
| Current (I) | 2 A | 3 A | 4 A |
Study the table.
- State whether the conductor used is ohmic or non-ohmic.
- Justify your answer.
- State Ohm's law.
A current of 3.2 mA flows through a conductor. If charge on an electron is - 1.6 × 10-19 coulomb, find the number of electrons that will pass each second through the cross section of that conductor.
