Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like, change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
उत्तर
Due to physical or chemical change, hydrogen bonding and various other attractive forces are disturbed, globules unfold and helix gets uncoiled to form a thread like molecule. Therefore, secondary and tertiary structure of protein loses all or part of their biological activity. This is called denaturation of proteins.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define the following as related to proteins:
Peptide linkage
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the α-helix structure of proteins?
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 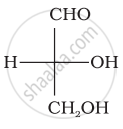 |
| (II) | 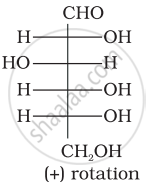 |
| (III) | 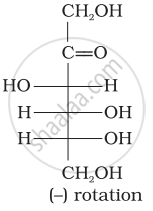 |
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
