Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Short Answer Question:
Explain the role of lactose in ‘Lac Operon’.
उत्तर
- A few molecules of lactose enter into the cell by an enzyme permease.
- A small amount of this enzyme is present even when the operon is switched off.
- A few molecules of lactose, act as inducer and bind to the repressor.
- This repressor – inducer complex fails to join with the operator gene, which is then turned on.
- Structural genes produce all enzymes. Thus, lactose acts as an inducer of its own breakdown.
- When the inducer level falls, the operator is blocked again by the repressor. So structural genes are repressed/inactivated again. This is negative feedback.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the components of lac operon and discuss their role.
Study the schematic representation of the genes involved in the lac operon given below and answer the questions that follow :
| p | i | p | o | z | y | a |
(a) Identify and name the regulatory gene in this operon. Explain its role in 'switching off' the operon.
(b) Why is the lac operon's regulation referred to as negative regulation?
(c) Name the inducer molecule and the products of the genes 'z' and 'y' of the operon. Write the functions of these gene products.
With respect to lac- operon explain the following terms:-
- regulator gene
- promoter gene
- structural gene
- inducer
Nucleic acids along with (i) and (ii) form the macromolecular fraction of the cell.
Which of the following gene is responsible for the synthesis of repressor in operon?
In which of the following conditions the lac operon in E. coli becomes "switched on"?
Lac operon consists of ______.
Which of the following is required as an inducer(s) for the expression of lac operon?
Explain the components of the structural genes in the Lac operon system in E.coli.
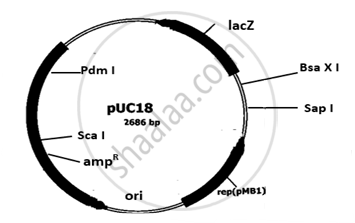
The diagram given below represents the image of the cloning vector pUC 18. The gene of interest is inserted and ligated within the gene lacZ. The recombinant DNA is introduced in the host bacterial cell. Explain the method that would help in selection of recombinant colonies from non-recombinant colonies.