Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically:
Maximize Z = 400x + 300y subject to x + y ≤ 200, x ≤ 40, x ≥ 20, y ≥ 0
उत्तर
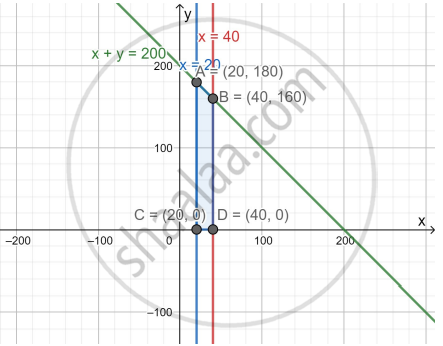
We have Z= 400x + 300y subject to x + y ≤ 200, x ≤ 40, x ≥ 20, y ≥ 0
The corner points of the feasible region are C(20, 0), D(40, 0), B(40, 160), A(20, 180)
| Corner Point | Z = 400x + 300y |
| C(20, 0) | 8000 |
| D(40, 0) | 16000 |
| B(40, 160) | 64000 |
| A(20, 180) | 62000 |
Maximum profit occurs at x = 40, y = 160 and the maximum profit = ₹ 64,000
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B'. 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs Rs 10 per kg and 'B' cost Rs 8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost
A manufacturing company makes two types of teaching aids A and B of Mathematics for class XII. Each type of A requires 9 labour hours for fabricating and 1 labour hour for finishing. Each type of B requires 12 labour hours for fabricating and 3 labour hours for finishing. For fabricating and finishing, the maximum labour hours available per week are 180 and 30, respectively. The company makes a profit of Rs 80 on each piece of type A and Rs 120 on each piece of type B. How many pieces of type A and type B should be manufactured per week to get maximum profit? Make it as an LPP and solve graphically. What is the maximum profit per week?
Maximize Z = 9x + 3y
Subject to
\[2x + 3y \leq 13\]
\[ 3x + y \leq 5\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 10x + 6y
Subject to
\[3x + y \leq 12\]
\[2x + 5y \leq 34\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
A diet is to contain at least 80 units of vitamin A and 100 units of minerals. Two foods F1and F2 are available. Food F1 costs Rs 4 per unit and F2 costs Rs 6 per unit one unit of food F1 contains 3 units of vitamin A and 4 units of minerals. One unit of food F2contains 6 units of vitamin A and 3 units of minerals. Formulate this as a linear programming problem and find graphically the minimum cost for diet that consists of mixture of these foods and also meets the mineral nutritional requirements
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food X and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B and 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y | 2 | 2 | 1 |
One kg of food X costs ₹16 and one kg of food Y costs ₹20. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the required diet?
A small manufacturer has employed 5 skilled men and 10 semi-skilled men and makes an article in two qualities deluxe model and an ordinary model. The making of a deluxe model requires 2 hrs. work by a skilled man and 2 hrs. work by a semi-skilled man. The ordinary model requires 1 hr by a skilled man and 3 hrs. by a semi-skilled man. By union rules no man may work more than 8 hrs per day. The manufacturers clear profit on deluxe model is Rs 15 and on an ordinary model is Rs 10. How many of each type should be made in order to maximize his total daily profit.
A factory owner purchases two types of machines, A and B, for his factory. The requirements and limitations for the machines are as follows:
| Area occupied by the machine |
Labour force for each machine |
Daily output in units |
|
| Machine A Machine B |
1000 sq. m 1200 sq. m |
12 men 8 men |
60 40 |
He has an area of 7600 sq. m available and 72 skilled men who can operate the machines.
How many machines of each type should he buy to maximize the daily output?
A firm manufacturing two types of electric items, A and B, can make a profit of Rs 20 per unit of A and Rs 30 per unit of B. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 4 transformers and each unit of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of these per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. Type B is an export model requiring a voltage stabilizer which has a supply restricted to 65 units per month. Formulate the linear programing problem for maximum profit and solve it graphically.
A chemical company produces two compounds, A and B. The following table gives the units of ingredients, C and D per kg of compounds A and B as well as minimum requirements of C and D and costs per kg of A and B. Find the quantities of A and B which would give a supply of C and D at a minimum cost.
| Compound | Minimum requirement | ||
| A | B | ||
| Ingredient C Ingredient D |
1 3 |
2 1 |
80 75 |
| Cost (in Rs) per kg | 4 | 6 | - |
A gardener has supply of fertilizer of type I which consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and type II fertilizer which consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, he finds that he needs at least 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for his crop. If the type I fertilizer costs 60 paise per kg and type II fertilizer costs 40 paise per kg, determine how many kilograms of each fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A producer has 30 and 17 units of labour and capital respectively which he can use to produce two type of goods x and y. To produce one unit of x, 2 units of labour and 3 units of capital are required. Similarly, 3 units of labour and 1 unit of capital is required to produce one unit of y. If x and y are priced at Rs 100 and Rs 120 per unit respectively, how should be producer use his resources to maximize the total revenue? Solve the problem graphically.
A manufacturer makes two products, A and B. Product A sells at Rs 200 each and takes 1/2 hour to make. Product B sells at Rs 300 each and takes 1 hour to make. There is a permanent order for 14 units of product A and 16 units of product B. A working week consists of 40 hours of production and the weekly turn over must not be less than Rs 10000. If the profit on each of product A is Rs 20 and an product B is Rs 30, then how many of each should be produced so that the profit is maximum? Also find the maximum profit.
A manufacturer has three machine I, II, III installed in his factory. Machines I and II are capable of being operated for at most 12 hours whereas machine III must be operated for atleast 5 hours a day. She produces only two items M and N each requiring the use of all the three machines.
The number of hours required for producing 1 unit each of M and N on the three machines are given in the following table:
| Items | Number of hours required on machines | ||
| I | II | III | |
| M | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| N | 2 | 1 | 1.25 |
She makes a profit of ₹600 and ₹400 on items M and N respectively. How many of each item should she produce so as to maximise her profit assuming that she can sell all the items that she produced? What will be the maximum profit?
There are two factories located one at place P and the other at place Q. From these locations, a certain commodity is to be delivered to each of the three depots situated at A, B and C. The weekly requirements of the depots are respectively 5, 5 and 4 units of the commodity while the production capacity of the factories at P and Q are respectively 8 and 6 units. The cost of transportation per unit is given below:
| From \ To | Cost (in ₹) | ||
| A | B | C | |
| P | 160 | 100 | 150 |
| Q | 100 | 120 | 100 |
How many units should be transported from each factory to each depot in order that the transportation cost is minimum. What will be the minimum transportation cost?
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of 200 passengers. A profit of ₹1000 is made on each executive class ticket and a profit of ₹600 is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves atleast 20 seats for executive class. However, atleast 4 times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class than by the executive class. Determine how many tickets of each type must be sold in order to maximise the profit of the airline. What is the maximum profit?
The point at which the maximum value of x + y subject to the constraints x + 2y ≤ 70, 2x + y ≤ 95, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is obtained, is ______.
Draw the graph of inequalities x ≤ 6, y −2 ≤ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 and indicate the feasible region
The region XOY - plane which is represented by the inequalities -5 ≤ x ≤ 5, -5 ≤ y ≤ 5 is ______
The maximum value of z = 3x + 10y subjected to the conditions 5x + 2y ≤ 10, 3x + 5y ≤ 15, x, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The point which provides the solution to the linear programming problem: Max P = 2x + 3y subject to constraints: x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 2x + 2y ≤ 9, 2x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 8, is ______
Corner points of the feasible region determined by the system of linear constraints are (0, 3), (1, 1) and (3, 0). Let Z = px + qy, where p, q > 0. Condition on p and q so that the minimum of Z occurs at (3, 0) and (1, 1) is ______.
In the Corner point method for solving a linear programming problem the second step after finding the feasible region of the linear programming problem and determining its corner points is ____________.
A feasible solution to a linear programming problem
Minimise z = – 3x + 4y subject to x + 2y ≤ 8, 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 What will be the minimum value of z ?
The solution set of the inequality 3x + 5y < 4 is ______.
The constraints –x1 + x2 ≤ 1, –x1 + 3x2 ≤ 9, x1x2 ≥ 0 define on ______.
The shaded part of given figure indicates in feasible region, then the constraints are:

Solve the following Linear Programming problem graphically:
Maximize: Z = 3x + 3.5y
Subject to constraints:
x + 2y ≥ 240,
3x + 1.5y ≥ 270,
1.5x + 2y ≤ 310,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
