Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
5.00858585
उत्तर
5.00858585 = 5.00858585
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Explain the term Saturated solution giving examples.
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when 1 mole of carbon is burnt in 16 g of dioxygen.
Calculate the amount of carbon dioxide that could be produced when 2 moles of carbon are burnt in 16 g of dioxygen.
If the density of methanol is 0.793 kg L–1, what is its volume needed for making 2.5 L of its 0.25 M solution?
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform, CHCl3, supposed to be carcinogenic in nature. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass).
- Express this in percent by mass.
- Determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
Calculate the molarity of a solution of ethanol in water in which the mole fraction of ethanol is 0.040 (assume the density of water to be one).
Why does the molarity of a solution depend upon temperature?
Solve the following problem:
Find out the molar mass of the following compounds:
Copper sulphate crystal (CuSO4.5H2O)
(At. mass: Cu = 63.5; S = 32; O = 16; H = 1; Na = 23; C = 12; Fe = 56; N = 14)
Solve the following problem:
Find out the molar mass of the following compounds:
Sodium carbonate, decahydrate (Na2CO3.10H2O)
(At. mass: Cu = 63.5; S = 32; O = 16; H = 1; Na = 23; C = 12; Fe = 56; N = 14)
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
3.49 × 10−11
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
3.75 × 10−1
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
0.011 × 10−3
Solve the following problem:
Perform the following calculation. Round off your answer to three digits.
`((9.28xx10^9)(9.9xx10^-7))/((511)(2.98xx10^-6))`
Name the process associated with the following
A drop of ink placed on the surface of water contained in a glass spreads throughout the water.
What are the favourable qualities given to gold when it is alloyed with copper or silver for the purpose of making ornaments?
Give an example of each mixture having the following characteristics. Suggest a suitable method to separate the components of this mixture
Two immiscible liquids.
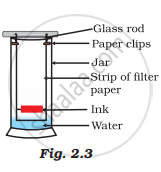
A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in Fig.2.3. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.
(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components?
(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
(iii) Suggest one more application of this technique.
What will be the molarity of a solution, which contains 5.85 g of NaCl(s) per 500 mL?
If 500 mL of a 5 M solution is diluted to 1500 mL, what will be the molarity of the solution obtained?
The molarity of pure water is ______.
An aqueous KCl solution of density 1.20 g mL-1 has a molality of 3.30 mol kg-1. The molarity of the solution in mol L-1 is ______. (Nearest integer)
What quantity (in mL) of a 45% acid solution of a monoprotic strong acid must be mixed with a 20% solution of the same acid to produce 800 mL of a 29.875% acid solution?
250 g solution of D-glucose in water contains 10.8% of carbon by weight. The molality of the solution is nearest to ______.
(Given: Atomic weights are H, 1u; C, 12u; O, 16u)
The molarity of urea (molar mass 60 g mol−1) solution by dissolving 15 g of urea in 500 cm3 of water is ______.
Find the molality of solution if boiling point increases by 1.75 K and molal elevation constant of solvent is 5K kg mol-1.
