Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State Lenz's Law.
उत्तर १
Lenz’s law: It is stated that the direction of induced e.m.f. is always in such direction that it opposes the change in magnetic flux.
`e=(d φ)/(dt)`
Consider a rectangular metal coil PQRS. Let ‘L’ be the length of the coil. It is placed in a partly magnetic field ‘B’. the direction of magnetic field is perpendicular to paper and into the paper. The ‘x’ part of the coil is in magnetic field at instant t. If the coil is moved towards right with a velocity v = dx/dt with help of external agent like hand. The magnetic flux through the coil is Φ= BA = BLx ∴Φ = B Lx -----(1) There is relative motion of a current through the coil. Let ‘i’ be current through the coil.
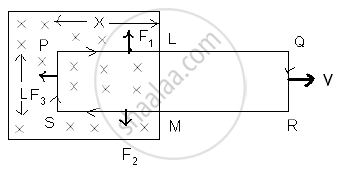
Three forces acts on the coil .
F1 on conductor PL ∴ F1 = Bix , vertically upward.
F2 on conductor MS ∴ F2 = Bix, vertically downward.
F3 on conductor SP ∴ F3 = BiL towards left.
F1 & F2 are equal and opposite and also in a same lines. They will cancel each other, F3 is a resultant force. The external agent has to do work against this force.
∴ F3 = - Bil -ve sign indicates that force is opposite to dx.
If dx is displacement in time dt, then work done dw = F3 dx
∴ dw = - BiL dx
This power is an electrical energy ‘ei’ where ‘e’ is an induced e.m.f.
`therefore ei=-(Bildx)/(dt)`
`therefore e=-(BLdx)/(dt)`
`therefore e= -BLv`
`therefore e=-d/dt (BLx)`
`therefore=e=-(d φ)/(dt)` from eq (1)
उत्तर २
The Lenz’s law states that the direction of induced current is such that it opposes the cause which produces it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State Faraday's laws of electromagnetic induction.
In the following diagram an arrow shows the motion of the coil towards the bar magnet.
(1) State in which direction the current flows, A to B or B to A?
(2) Name the law used to come to the conclusion.

- How would you demonstrate that a momentary current can be obtained by the suitable use of a magnet, a coil of wire and a galvanometer?
- What is the source of energy associated with the current obtained in part (a)?
- Describe briefly one way producing an induced e.m.f?
- State one factor that determines the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in part (a) above.
- What factor determines the direction of induced e.m.f. in part (a) above?
What is Lenz’s law?
Why does it become more difficult to move a magnet towards a coil when the number of turns in the coil has been increased?
The direction of induced current is obtained by ______.
Explain the principle, construction and working of a dc motor.
Faraday's law is the consequence of conservation of ______
The instantaneous magnetic flux in a circuit is `phi=4t^2-4t+1`. The total resistance of circuit is 15 Ω. At t = 2s, the induced current in circuit is ____________.
An electron moves on a straight line path XY as shown. The abed is a coil adjacent to the path of electron. What will be the direction of current, if any, induced in the coil?

In a coil of resistance 150 `Omega`, a current is induced by changing the magnetic flux through it as shown in the figure. The magnitude of change in flux through the coil is ____________.
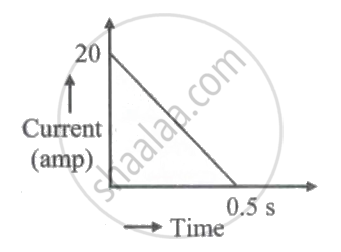
Magnetic flux passing through a coil is initially 6 x 10-4 Wb. It reduces to 10 % of its original value in 't' second. If the e.m.f. induced is 0.54 mV then 't' in second is ____________.
A magnet is moved towards a coil (i) quickly (ii) slowly. The induced potential difference.
Fleming’s left hand and Right hand rules are used in ____________.
The direction of the magnetic field around a straight conductor carrying current can be determined by ______.
The laws of induction were given by ______.
Define the right-hand thumb rule.
Two vectors `vec"A"` and `vec"B"` have equal magnitudes. If magnitude of `vec"A"` + `vec"B"` is equal to two times the magnitude of `vec"A"` - `vec"B"`, then the angle between `vec"A"` and `vec"B"` will be ______.
For which angle between two equal vectors `vec"A"` and `vec"B"` will the magnitude of the sum of two vectors be equal to the magnitude of each vector?
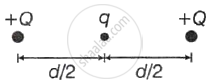
Two positively charged particles each having charge Q and are d distance apart. A third charge is introduced in midway on the line joining the two. Find nature and magnitude of third charge, so that the system is in equilibrium ______.
Express Faraday-Lenz's law of electromagnetic induction in an equation form.
A conductor in the form of a circular arc of the radius of curvature R subtends an angle Ø at its centre of curvature. If the current in the conduct is I, the magnetic induction at the centre of curvature is ______.
A circular loop is placed in a uniform magnetic field. The total number of magnetic field lines passing normally through the plane of the coil is called ______.
Name the principle of AC generator.
State the use of the principle of electromagnetic induction.
State two factors on which the magnitude of induced e.m.f. in a coil depend.
