Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the meaning and properties of production possibilities frontier.
उत्तर
PPC is the curve which shows the combinations of two goods and services that can be produced with a fuller utilisation of a given amount of resources in the most efficient way and with a given production technology.
Properties of PPC
1) Concave to the origin: PPC curve is concave to the origin. This is because of the increasing opportunity cost i.e. in accordance with the law of increasing opportunity cost.
2) Downward sloping curve: PPC curve is downward sloping from left to right. This is because the production of every additional unit of one good, more and more units of other good has to be sacrificed.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium using indifference curve analysis.
Explain the three properties of the indifference curves.
If Marginal Rate of Substitution is constant throughout, the Indifference curve will be :(choose the correct alternative)
a. Parallel to the x-axis.
b. Downward sloping concave.
c. Downward sloping convex.
d. Downward sloping straight line.
If Marginal Rate of Substitution is increasing throughout, the Indifference Curve will be: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Downward sloping convex
b. Downward sloping concave
c. Downward sloping straight line
d. Upward sloping convex
A consumer consumes only two goods. If the price of one of the goods falls, the indifference curve: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Shifts upwards
b. Shifts downwards
c. Can shift both upwards or downwards
d. Does not shift
Explain why is an indifference curve is Convex.
Define an indifference map. Why does indifference curve to the right show more utility? Explain.
What are the properties of indifference curves?
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Columns I | Columns II |
| (1) Demand Curve | (a) Downward sloping |
| (2) Indifference curve | (b) Upward rising |
| (3) Marginal Utility Curve | (c) L shaped curve |
| (4) Total Utility Curve | (d) Y shaped curve |
"Higher indifference curve represents fewer quantities of one or both goods, a higher indifference curve shows higher utility level." Choose the correct option for the above mentioned statement:
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Column I | Column II |
| (1) Monotonic Preferences | (a) Consumer preferences are called monotonic when between any three bundles, consumers always choose a bundle having more of one good and no less of other goods. |
| (2) Indifference Set | (b) It is a set of those divisions of two goods that offer the consumer the same level of satisfaction so that the consumer is indifferent across any number of combinations in his indifference set. |
| (3) Indifference Curve | (c) It is a curve showing the different combinations of two goods, each combination offering the same level of satisfaction to the consumer. |
| (4) Indifference Map | (d) It refers to a set of indifference curves placed in different diagrams for the same type of goods. |
Indifference curve is:
Which of the following is an assumption for Indifference Curve Approach.
Observe the graph given below and answer the question that follow.
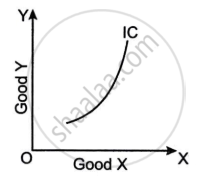
- Give a reason to explain if the graph shown above can be a common phenomenon or not. [2]
- What is an indifference map? Draw its diagram. [2]
- State any two differences between cardinal utility and ordinal utility. [2]
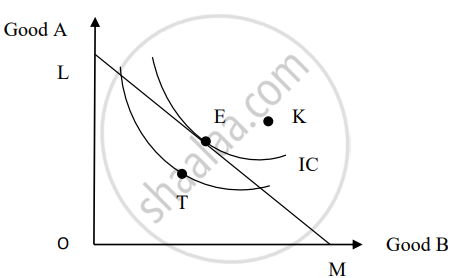
Points K and T will NOT be attained by the consumer. Select the reason from the options given below.
