Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two effects of a force when applied on a body.
उत्तर १
Two effects of applied force:
- It can change the state of body.
i.e. It can stop a moving object and also a force can move a stationary object. - A force can change the shape (and size) of an object.
उत्तर २
-
Change in Motion:
- A force can make a stationary body move or change the speed and direction of a moving body.
- Example: Pushing a stationary car causes it to start moving.
-
Change in Shape or Size:
- A force can deform an object, altering its shape or size.
- Example: Squeezing a rubber ball changes its shape temporarily.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define force. State its S.I. unit.
Find the moment of force of 20 N about an axis of rotation at distance 0.5 m from the force.
The moment of a force about axis depends ______.
A nut is opened by a wrench of length 10 cm. if the least force required is 5.0 N. find the moment of force needed to turn the nut.
A steering wheel of diameter 0.5 m is rotated anticlockwise by applying two forces each of magnitude 6 N. Draw a diagram to show the application of forces and calculate the moment of forces applied.
Calculate the resultant moment of forces about O and state its direction in fig.
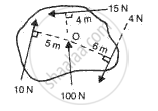
Fig. shows a uniform meter scale weighing 100 N pivoted at its centre. Two weights of 500 N and 300 N are hung from the ruler as shown in fig.
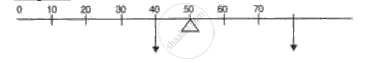
(i) Calculate total clockwise and anticlockwise moments.
(ii) Calculate difference in clockwise moment and anticlockwise moment.
(iii) Calculate the distance from O where a 100 N weight should be suspended to balance the meter scale.
A meter scale is provided at 10 cm mark and is balanced by suspending 400 g from 0 cm mark (fig. ). Calculate the mass of meter scale.

State whether the moment of force is a scalar or vector quantity?
The perpendicular distance between the point of application of force and turning point is 1.75 m when a force of 80 N acts on a rigid body. Calculate the moment of force.
