Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Sulphuric acid reacts with sodium hydroxide as follows:
\[\ce{H2SO4 + 2NaOH -> Na2SO4 + 2H2O}\]
When 1 L of 0.1 M sulphuric acid solution is allowed to react with 1 L of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide solution, the amount of sodium sulphate formed and its molarity in the solution obtained is:
(i) 0.1 mol L–1
(ii) 7.10 g
(iii) 0.025 mol L–1
(iv) 3.55 g
उत्तर
(ii) 7.10 g
(iii) 0.025 mol L–1
Explanation:
0.1 mole \[\ce{H2SO4}\] reacts with 1 mole of \[\ce{NaOH}\].
0.1 mole of \[\ce{NaOH}\] will react with `0.1/2` mole of \[\ce{H2SO4}\].
Here, \[\ce{NaOH}\] is the limiting reagent.
2 mole of \[\ce{NaOH}\] produces 1 mole of \[\ce{Na2SO4}\].
0.1 mole of \[\ce{NaOH}\] will give `0.1/2` mole of \[\ce{Na2SO4}\].
No. of mole = `"Given mass"/("Molar mass" (Na_2SO_4))`
On substituting the value in tha above equation, the mass can be calculated as 0.05 mol = `"Given mass"/(142 g mol^-1)`
Given mass = 7.10 g
Volume of solution after mixing is 2 L.
So, the molarity of \[\ce{Na2SO4}\] is,
Molarity = `0.05/2` = 0.025 mol L–1
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform, CHCl3, supposed to be carcinogenic in nature. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass).
- Express this in percent by mass.
- Determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
To make a saturated solution, 36 g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100 g of water at 293 K. Find its concentration at this temperature.
Solve the following problem:
Write the following number in ordinary decimal form:
43.71 × 10−4
Solve the following problem:
The hourly energy requirements of an astronaut can be satisfied by the energy released when 34 grams of sucrose are “burnt” in his body. How many grams of oxygen would be needed to be carried in space capsule to meet his requirement for one day?
Name the process associated with the following
A drop of ink placed on the surface of water contained in a glass spreads throughout the water.
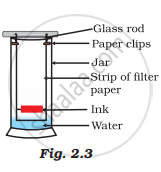
A child wanted to separate the mixture of dyes constituting a sample of ink. He marked a line by the ink on the filter paper and placed the filter paper in a glass containing water as shown in Fig.2.3. The filter paper was removed when the water moved near the top of the filter paper.
(i) What would you expect to see, if the ink contains three different coloured components?
(ii) Name the technique used by the child.
(iii) Suggest one more application of this technique.
Match the following physical quantities with units
| Physical quantity | Unit |
| (i) Molarity | (a) g mL–1 |
| (ii) Mole fraction | (b) mol |
| (iii) Mole | (c) Pascal |
| (iv) Molality | (d) Unitless |
| (v) Pressure | (e) mol L–1 |
| (vi) Luminous intensity | (f) Candela |
| (vii) Density | (g) mol kg–1 |
| (viii) Mass | (h) Nm–1 |
| (i) kg |
250 g solution of D-glucose in water contains 10.8% of carbon by weight. The molality of the solution is nearest to ______.
(Given: Atomic weights are H, 1u; C, 12u; O, 16u)
Find the molality of solution if boiling point increases by 1.75 K and molal elevation constant of solvent is 5K kg mol-1.
