Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The carrier wave is represented by
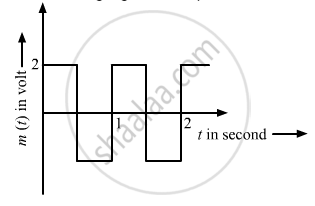
उत्तर
Modulation index (\[\mu\]) is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier wave. The generalised equation of a carrier wave is given below: \[c(t) = A_c \sin \omega_c t\]
The generalised equation of a modulating wave is given below:
\[c_m (t) = A_c \sin \omega_c t + \mu A_c \sin \omega_m t\sin \omega_c t\]
Here,
Amplitude of modulating signal,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The process of superimposing a low frequency signal on a high frequency wave is_______ .
Explain the need for modulation related to the size of antenna (aerial).
Why is Modulation index kept low?
What is the role of a bandpass filter?
A carrier wave of peak voltage 15 V is used to transmit a message signal. Find the peak voltage of the modulating signal in order to have a modulation index of 60%
In the block diagram of a simple modulator for obtaining an AM signal, shown in the figure, identify the boxes A and B. Write their function.
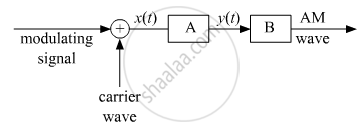
Answer the following question.
Why a signal transmitted from a TV tower cannot be received beyond a certain distance? Write the expression for the optimum separation between the receiving and the transmitting antenna.
Broadcasting antennas are generally ______.
An audio signal of 15kHz frequency cannot be transmitted over long distances without modulation because ______.
- the size of the required antenna would be at least 5 km which is not convenient.
- the audio signal can not be transmitted through sky waves.
- the size of the required antenna would be at least 20 km, which is not convenient.
- effective power transmitted would be very low, if the size of the antenna is less than 5 km.
A 25 m long antenna is mounted on an antenna tower. The height of the antenna tower is 75 m. The wavelength (in meter) of the signal transmitted by this antenna would be ______.
