Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
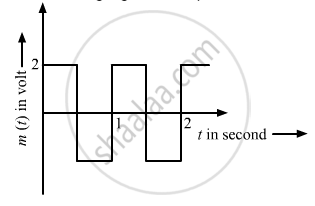
The carrier wave is represented by
उत्तर
Modulation index (\[\mu\]) is the ratio of the amplitude of the modulating signal to the amplitude of the carrier wave. The generalised equation of a carrier wave is given below: \[c(t) = A_c \sin \omega_c t\]
The generalised equation of a modulating wave is given below:
\[c_m (t) = A_c \sin \omega_c t + \mu A_c \sin \omega_m t\sin \omega_c t\]
Here,
Amplitude of modulating signal,
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Define modulation index.
Why is Modulation index kept low?
What is the role of a bandpass filter?
In a communication system, what is meant by modulation?
Answer the following question.
Why a signal transmitted from a TV tower cannot be received beyond a certain distance? Write the expression for the optimum separation between the receiving and the transmitting antenna.
A 20 volt AC is applied to a circuit consisting of a resistance and a coil with negligible resistance. If the voltage across the resistance is 12 volt, the voltage across the coil is ______.
Broadcasting antennas are generally ______.
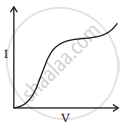
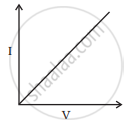
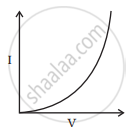
I-V characteristics of four devices are shown in Figures.
 |
 |
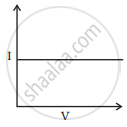 |
|
| (i) | (ii) | (iii) | (iv) |
Identify devices that can be used for modulation.
A carrier wave Vc(t) = 160 sin(2π × 106t) volts is made to vary between Vmax = 200 V and Vmin = 120 V by a message signal Vm(t) = Am sin(2π × 103t) volts. The peak voltage Am of the modulating signal is ______.
A transmitting antenna has a height of 320 m and that of receiving antenna is 2000 m. The maximum distance between them for satisfactory communication in line of sight mode is 'd'. The value of 'd' is ______ km.