Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because ______.
विकल्प
number density of free current carriers increases.
relaxation time increases.
both number density of carriers and relaxation time increase.
number density of current carriers increases, relaxation time decreases but effect of decrease in relaxation time is much less than increase in number density.
उत्तर
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because number density of current carriers increases, relaxation time decreases but effect of decrease in relaxation time is much less than increase in number density.
Explanation:
The conductivity of Semiconductor:
(1) In intrinsic semiconductors ne = nh. Both electrons and holes contribute to current conduction.
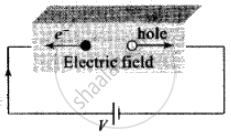
(2) When some potential difference is applied across a piece of intrinsic semiconductor current flows in it due to both electrons and holes, i.e. `i = i_e + i_h` ⇒ `eA[n_ev_e + n_hv_h]`
(3) As we know `σ = J/E = i/(AE)`. Hence conductivity of semiconductor is `σ = e[n_eu_e + n_hu_h]`; where `v_e` = drift velocity of electron, `v_h` = drift velocity of holes, E = Applied electric field, `mu_e = v_e/E` = mobility of electron and `mu_h = v_h/E` = mobility of holes.
(4) Motion of electrons in the conduction band and of holes in the valence band under the action of electric field is shown below:
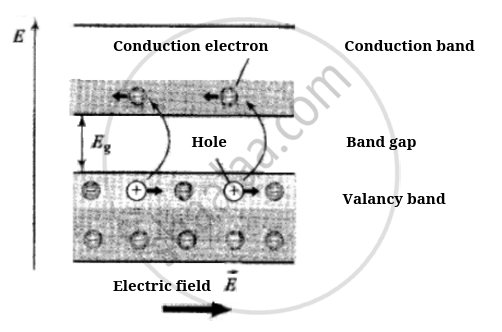
(5) At absolute zero temperature (0 K) conduction band of the semiconductor is completely empty, i.e., σ > 0. Hence the semiconductor behaves as an insulator.
We know that `σ = (n e^2τ)/m`,
So, `σ ∝ nτ`
Where n = number density and τ = relaxation time
In semiconductors, conductivity increases with increase in temperature, because the number density of current carries increases, relaxation time decreases but effect of decrease in relaxation is much less than increase in number density.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A donor impurity results in ______.
In p-type semiconductor, ______.
State how a p-type semiconductor will be obtained from a pure crystal of a semiconductor.
Distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors.
Why are elemental dopants for Silicon or Germanium usually chosen from group XIII or group XV?
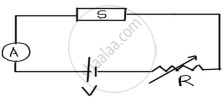
The figure shows a piece of pure semiconductor S in series with a variable resistor R and a source of constant voltage V. Should the value of R be increased or decreased to keep the reading of the ammeter constant, when semiconductor S is heated? Justify your answer
Name the extrinsic semiconductors formed when pure germanium is doped with a Pentavalent impurity. Draw the energy band diagram of extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
In an extrinsic semiconductor, the number density of holes is 4 × 1020 m-3. If the number density of intrinsic carriers is 1.2 × 1015 m-3, the number density of electrons in it is ______.
- Assertion (A): Putting the p-type semiconductor slab directly in physical contact with the n-type semiconductor slab cannot form the pn junction.
- Reason (R): The roughness at contact will be much more than inter atomic crystal spacing and continuous flow of charge carriers is not possible.
What type of semiconductor is obtained when a crystal of silicon is doped with a trivalent element?
