Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because ______.
Options
number density of free current carriers increases.
relaxation time increases.
both number density of carriers and relaxation time increase.
number density of current carriers increases, relaxation time decreases but effect of decrease in relaxation time is much less than increase in number density.
Solution
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because number density of current carriers increases, relaxation time decreases but effect of decrease in relaxation time is much less than increase in number density.
Explanation:
The conductivity of Semiconductor:
(1) In intrinsic semiconductors ne = nh. Both electrons and holes contribute to current conduction.
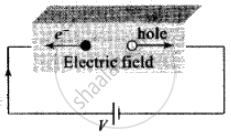
(2) When some potential difference is applied across a piece of intrinsic semiconductor current flows in it due to both electrons and holes, i.e. `i = i_e + i_h` ⇒ `eA[n_ev_e + n_hv_h]`
(3) As we know `σ = J/E = i/(AE)`. Hence conductivity of semiconductor is `σ = e[n_eu_e + n_hu_h]`; where `v_e` = drift velocity of electron, `v_h` = drift velocity of holes, E = Applied electric field, `mu_e = v_e/E` = mobility of electron and `mu_h = v_h/E` = mobility of holes.
(4) Motion of electrons in the conduction band and of holes in the valence band under the action of electric field is shown below:
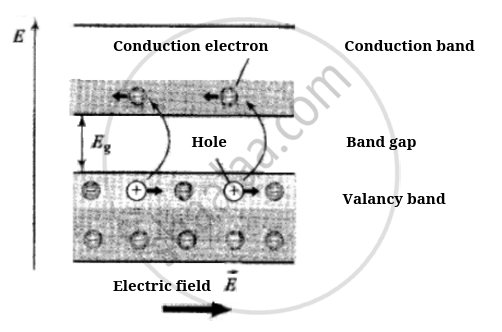
(5) At absolute zero temperature (0 K) conduction band of the semiconductor is completely empty, i.e., σ > 0. Hence the semiconductor behaves as an insulator.
We know that `σ = (n e^2τ)/m`,
So, `σ ∝ nτ`
Where n = number density and τ = relaxation time
In semiconductors, conductivity increases with increase in temperature, because the number density of current carries increases, relaxation time decreases but effect of decrease in relaxation is much less than increase in number density.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Electronic configuration of germanium is 2, 8, 18 and 4. To make it extrinsic semiconductor small quantity of antimony is added. The correct statement is ____________.
When p-n junction diode is forward biased, then ______.
In p-type semiconductor, ______.
State how a p-type semiconductor will be obtained from a pure crystal of a semiconductor.
Distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors.
Suppose a ‘n’-type wafer is created by doping Si crystal having 5 × 1028 atoms/m3 with 1 ppm concentration of As. On the surface 200 ppm Boron is added to create ‘P’ region in this wafer. Considering n i = 1.5 × 1016 m–3, (i) Calculate the densities of the charge carriers in the n and p regions. (ii) Comment which charge carriers would contribute largely for the reverse saturation current when diode is reverse biased.
Name the extrinsic semiconductors formed when pure germanium is doped with a Pentavalent impurity. Draw the energy band diagram of extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
Pieces of copper and of silicon are initially at room temperature. Both are heated to temperature T. The conductivity of ______.
- Assertion (A): Putting the p-type semiconductor slab directly in physical contact with the n-type semiconductor slab cannot form the pn junction.
- Reason (R): The roughness at contact will be much more than inter atomic crystal spacing and continuous flow of charge carriers is not possible.
The majority charge carriers in a P-type semiconductor are ______.
