Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
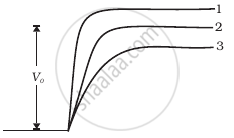
Options
1 and 3 both correspond to forward bias of junction.
3 corresponds to forward bias of junction and 1 corresponds to reverse bias of junction.
1 corresponds to forward bias and 3 corresponds to reverse bias of junction.
3 and 1 both correspond to reverse bias of junction.
Solution
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction 3 corresponds to forward bias of junction and 1 corresponds to reverse bias of junction.
Explanation:
P-N Junction Diode: When a P-type semiconductor is suitably joined to an N-type semiconductor, then the resulting arrangement is called a P-N junction or P-N junction diode.
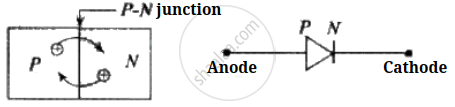
(1) Depletion region: On account of the difference in concentration of charge carrier in the two sections of the P-N junction, the electrons from N-region diffuse through the junction into P-region and the hole from the P region diffuses into N-region.
Due to diffusion, the neutrality of both N and P-type semiconductor is disturbed and a layer of negatively charged ions appear near the junction in the P-crystal and a layer of positive ions appears near the junction in N-crystal. This layer is called the depletion layer.
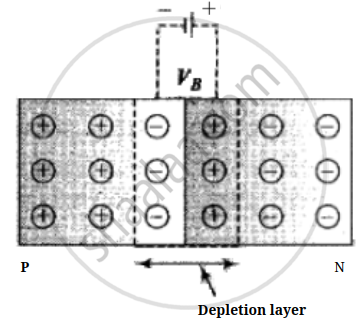
- The thickness of the depletion layer is 1 micron = 10–6 m.
- Width of the depletion layer ∝ `1/"Dopping"`
- Depletion is directly proportional to temperature.
- The P-N junction diode is equivalent to the capacitor in which the depletion layer acts as a dielectric.
(2) Potential barrier: The potential difference created across the P-N junction due to the diffusion of electrons and holes is called the potential barrier.
For Ge, VB = 0.3 V and for silicon VB = 0. 7 V
On average the potential barrier in a P-N junction is – 0.5 V and the width of the depletion region = 10–6m.
So the barrier electric field `E = V/d = 0.5/10^-6 = 5 xx 10^5` V/m
The height of the potential barrier is decreased when the p-n junction is forward biased, it opposes the potential barrier junction when the p-n junction is reverse biased and it supports the potential barrier junction, resulting increase in the potential barrier across the junction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
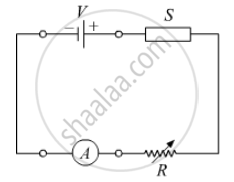
In the following diagram 'S' is a semiconductor. Would you increase or decrease the value of R to keep the reading of the ammeter A constant when S is heated? Give reason for your answer.
What is the use of Zener diode?
In a photo diode, the conductive increases when the material is exposed to light. It is found that the conductivity changes only if the wavelength is less than 620 nm. What is the band gap?
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
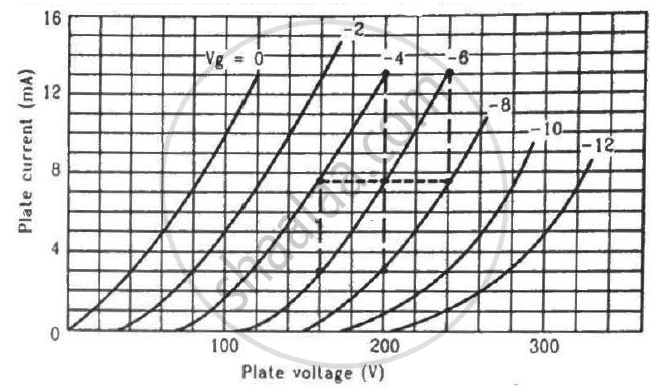
Find the values of rp, µ and gm of a triode operating at plate voltage 200 V and grid voltage −6. The plate characteristics are shown in the figure.
With reference to Semiconductor Physics,
Name the diode that emits spontaneous radiation when forward biased.
The drift current in a p-n junction is from the ______.
On increasing the reverse biases voltage to a large value in a P – N junction diode-current
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
When an electric field is applied across a semiconductor ______.
- electrons move from lower energy level to higher energy level in the conduction band.
- electrons move from higher energy level to lower energy level in the conduction band.
- holes in the valence band move from higher energy level to lower energy level.
- holes in the valence band move from lower energy level to higher energy level.
Draw the circuit arrangement for studying V-I characteristics of a p-n junction diode in (i) forward biasing and (ii) reverse biasing. Draw the typical V-I characteristics of a silicon diode.
