Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
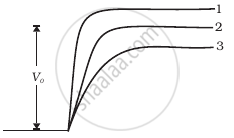
पर्याय
1 and 3 both correspond to forward bias of junction.
3 corresponds to forward bias of junction and 1 corresponds to reverse bias of junction.
1 corresponds to forward bias and 3 corresponds to reverse bias of junction.
3 and 1 both correspond to reverse bias of junction.
उत्तर
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction 3 corresponds to forward bias of junction and 1 corresponds to reverse bias of junction.
Explanation:
P-N Junction Diode: When a P-type semiconductor is suitably joined to an N-type semiconductor, then the resulting arrangement is called a P-N junction or P-N junction diode.
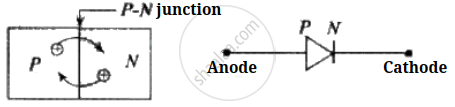
(1) Depletion region: On account of the difference in concentration of charge carrier in the two sections of the P-N junction, the electrons from N-region diffuse through the junction into P-region and the hole from the P region diffuses into N-region.
Due to diffusion, the neutrality of both N and P-type semiconductor is disturbed and a layer of negatively charged ions appear near the junction in the P-crystal and a layer of positive ions appears near the junction in N-crystal. This layer is called the depletion layer.
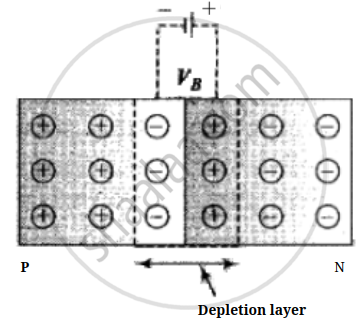
- The thickness of the depletion layer is 1 micron = 10–6 m.
- Width of the depletion layer ∝ `1/"Dopping"`
- Depletion is directly proportional to temperature.
- The P-N junction diode is equivalent to the capacitor in which the depletion layer acts as a dielectric.
(2) Potential barrier: The potential difference created across the P-N junction due to the diffusion of electrons and holes is called the potential barrier.
For Ge, VB = 0.3 V and for silicon VB = 0. 7 V
On average the potential barrier in a P-N junction is – 0.5 V and the width of the depletion region = 10–6m.
So the barrier electric field `E = V/d = 0.5/10^-6 = 5 xx 10^5` V/m
The height of the potential barrier is decreased when the p-n junction is forward biased, it opposes the potential barrier junction when the p-n junction is reverse biased and it supports the potential barrier junction, resulting increase in the potential barrier across the junction.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Plot a graph showing variation of current versus voltage for the material GaAs ?
Show on a graph, the variation of resistivity with temperature for a typical semiconductor.
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
In semiconductor physics, what is meant by:
(i) rectifier
(ii) an amplifier
(iii) an oscillator
Basic materials used in the present solid state electronic devices like diode, transistor, ICs, etc are ______.
Diffusion in a p-n junction is due to ______.
Avalanche breakdown is due to ______.
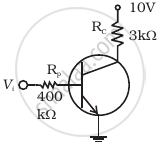
In the circuit shown in figure, when the input voltage of the base resistance is 10 V, Vbe is zero and Vce is also zero. Find the values of Ib, Ic and β.
Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
An ideal PN junction diode offers ______.
