Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With reference to a semiconductor diode, what is meant by:
(i) Forward bias
(ii) Reverse bias
(iii) Depletion region
उत्तर
(i) Forward bias: When a battery' is connected to a p-n diode such that the current is in the direction of diode current, the arrangement is called forward bias.
(ii) Reverse bias: If the current flows opposite to the direction of diode current, this is called reverse bias.
(iii) Depletion region: In a p-n diode, the region in which electrons and holes neutralize each other is called depletion region or zone.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With reference to semiconductor devices, define a p-type semiconductor and a Zener diode.
The plate current in a diode is 20 mA when the plate voltage is 50 V or 60 V. What will be the current if the plate voltage is 70 V?
The power delivered in the plate circular of a diode is 1.0 W when the plate voltage is 36 V. Find the power delivered if the plate voltage is increased to 49 V. Assume Langmuir-Child equation to hold.
A triode value operates at Vp = 225 V and Vg = −0.5 V.
The plate current remains unchanged if the plate voltage is increased to 250 V and the grid voltage is decreased to −2.5 V. Calculate the amplification factor.
Basic materials used in the present solid state electronic devices like diode, transistor, ICs, etc are ______.
In Figure, Vo is the potential barrier across a p-n junction, when no battery is connected across the junction ______.
In the circuit shown in figure, if the diode forward voltage drop is 0.3 V, the voltage difference between A and B is ______.

Draw V-I characteristics of a p-n Junction diode.
Read the following paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
| A semiconductor diode is basically a pn junction with metallic contacts provided at the ends for the application of an external voltage. It is a two-terminal device. When an external voltage is applied across a semiconductor diode such that the p-side is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and the n-side to the negative terminal, it is said to be forward-biased. When an external voltage is applied across the diode such that the n-side is positive and the p-side is negative, it is said to be reverse-biased. An ideal diode is one whose resistance in forward biasing is zero and the resistance is infinite in reverse biasing. When the diode is forward biased, it is found that beyond forward voltage called knee voltage, the conductivity is very high. When the biasing voltage is more than the knee voltage the potential barrier is overcome and the current increases rapidly with an increase in forward voltage. When the diode is reverse biased, the reverse bias voltage produces a very small current of about a few microamperes which almost remains constant with bias. This small current is a reverse saturation current. |
- In the given figure, a diode D is connected to an external resistance R = 100 Ω and an emf of 3.5 V. If the barrier potential developed across the diode is 0.5 V, the current in the circuit will be:

(a) 40 mA
(b) 20 mA
(c) 35 mA
(d) 30 mA - In which of the following figures, the pn diode is reverse biased?
(a)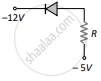
(b)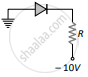
(c)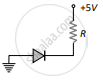
(d)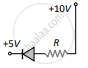
- Based on the V-I characteristics of the diode, we can classify the diode as:
(a) bilateral device
(b) ohmic device
(c) non-ohmic device
(d) passive element
OR
Two identical PN junctions can be connected in series by three different methods as shown in the figure. If the potential difference in the junctions is the same, then the correct connections will be:
(a) in the circuits (1) and (2)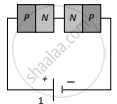
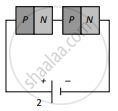
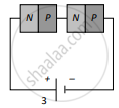
(b) in the circuits (2) and (3)
(c) in the circuits (1) and (3)
(d) only in the circuit (1) 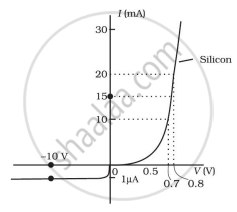
The V-I characteristic of a diode is shown in the figure. The ratio of the resistance of the diode at I = 15 mA to the resistance at V = -10 V is
(a) 100
(b) 106
(c) 10
(d) 10-6
With reference to a semiconductor diode, define the potential barrier.
