Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In Figure, assuming the diodes to be ideal ______.

Options
D1 is forward biased and D2 is reverse biased and hence current flows from A to B.
D2 is forward biased and D1 is reverse biased and hence no current flows from B to A and vice versa.
D1 and D2 are both forward biased and hence current flows from A to B.
D1 and D2 are both reverse biased and hence no current flows from A to B and vice versa.
Solution
In Figure, assuming the diodes to be ideal D2 is forward biased and D1 is reverse biased and hence no current flows from B to A and vice versa.
Explanation:
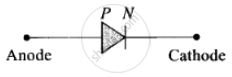
A symbol of the diode is represented like this: In this problem first, we have to check the polarity of the diodes. –10 V is the lower voltage in the circuit. Now p-side of p-n Anode Cathode junction D1 is connected to lower voltage and n-side of D1 to the higher voltage. Thus D1 is reverse biased.
Now, let us analyse 2nd diode of the given circuit. The p-side of p-n junction D2 is at higher potential and n-side of D2 is at lower potential. Therefore D2 is forward biased.
Hence, the current flows through the junction from B to A.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Colour of light emitted by LED depends upon__________________ .
- its forward bias
- its reverse bias
- the band gap of the material of semiconductor
- its size
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Forward biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
Write briefly the important processes that occur during the formation of p−n junction. With the help of necessary diagrams, explain the term 'barrier potential'.
The current in the forward bias is known to be more (~mA) than the current in the reverse bias (~μA). What is the reason, then, to operate the photodiode in reverse bias?
Explain the formation of depletion layer and potential barrier in a p−n junction.
Write the important considerations which are to be taken into account while fabricating a p-n junction diode to be used as a Light Emitting Diode (LED). What should be the order of band gap of an LED, if it is required to emit light in the visible range? Draw a circuit diagram and explain its action.
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with a band gap of 2.5 eV. lt can detect a signal of wavelength ______.
Which one of the following is not the advantage of LED?
Briefly explain how emf is generated in a solar cell.
What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell?
