Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
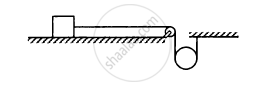
The descending pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2. The fixed pulley is light and the horizontal plane frictionless. Find the acceleration of the block if its mass is 1⋅0 kg.
उत्तर
Let the mass of block be m1 and mass of pulley be m2.
Acceleration of the massive pulley will be half of that of the block.
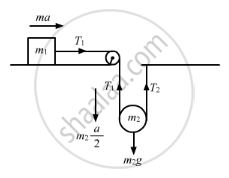
From the free body diagram, we have
\[T_1 = m_1 a..........(1)\]
\[\left( T_2 - T_1 \right) r = I\alpha\]
\[ T_2 - T_1 = \frac{Ia}{2 r^2} = \frac{5a}{2}..........(2)\]
\[ m_2 g - m_2 \frac{a}{2} = T_1 + T_2............(3)\]
Putting the value of mass in equation (1) and using equation (1) in equation (2), we get
\[T_1 = a\text{ and }T_2 = \frac{7}{2}a\]
\[m_2 g = m_2 \frac{a}{2} + \frac{7}{2}a + a\]
On replacing the value of \[m_2 using\frac{1}{2}m r^2 = I,\] we get
\[\frac{2I}{r^2}g = \frac{2I}{r^2}\frac{a}{2} + \frac{9}{2}a\]
\[ \Rightarrow 98 = 5a + 4 . 5a\]
\[ \Rightarrow a = \frac{98}{9 . 5} = 10 . 3 m/ s^2\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Torques of equal magnitude are applied to a hollow cylinder and a solid sphere, both having the same mass and radius. The cylinder is free to rotate about its standard axis of symmetry, and the sphere is free to rotate about an axis passing through its centre. Which of the two will acquire a greater angular speed after a given time?
A rope of negligible mass is wound round a hollow cylinder of mass 3 kg and radius 40 cm. What is the angular acceleration of the cylinder if the rope is pulled with a force of 30 N? What is the linear acceleration of the rope? Assume that there is no slipping.
A solid cylinder rolls up an inclined plane of angle of inclination 30°. At the bottom of the inclined plane, the centre of mass of the cylinder has a speed of 5 m/s.
(a) How far will the cylinder go up the plane?
(b) How long will it take to return to the bottom?
Two discs of moments of inertia I1 and I2 about their respective axes (normal to the disc and passing through the centre), and rotating with angular speeds ω1 and ω2 are brought into contact face to face with their axes of rotation coincident. (a) What is the angular speed of the two-disc system? (b) Show that the kinetic energy of the combined system is less than the sum of the initial kinetic energies of the two discs. How do you account for this loss in energy? Take ω1 ≠ ω2.
A cylinder of mass 10 kg and radius 15 cm is rolling perfectly on a plane of inclination 30°. The coefficient of static friction µs = 0.25.
(a) How much is the force of friction acting on the cylinder?
(b) What is the work done against friction during rolling?
(c) If the inclination θ of the plane is increased, at what value of θ does the cylinder begin to skid, and not roll perfectly?
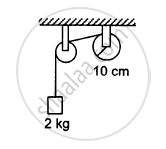
A string is wrapped on a wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅20 kg-m2 and radius 10 cm and goes through a light pulley to support a block of mass 2⋅0 kg as shown in the following figure. Find the acceleration of the block.
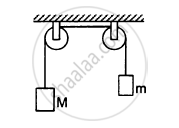
The pulleys shown in the following figure are identical, each having a radius R and moment of inertia I. Find the acceleration of the block M.
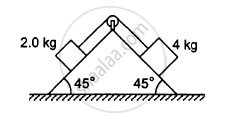
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius 10 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅5 kg-m2about its axis. Assuming the inclined planes to be frictionless, calculate the acceleration of the 4⋅0 kg block.
A wheel of moment of inertia 0⋅500 kg-m2 and radius 20⋅0 cm is rotating about its axis at an angular speed of 20⋅0 rad/s. It picks up a stationary particle of mass 200 g at its edge. Find the new angular speed of the wheel.
A boy is seated in a revolving chair revolving at an angular speed of 120 revolutions per minute. Two heavy balls form part of the revolving system and the boy can pull the balls closer to himself or may push them apart. If by pulling the balls closer, the boy decreases the moment of inertia of the system from 6 kg-m2 to 2 kg-m2, what will be the new angular speed?
A kid of mass M stands at the edge of a platform of radius R which can be freely rotated about its axis. The moment of inertia of the platform is I. The system is at rest when a friend throws a ball of mass m and the kid catches it. If the velocity of the ball is \[\nu\] horizontally along the tangent to the edge of the platform when it was caught by the kid, find the angular speed of the platform after the event.
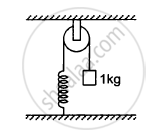
The pulley shown in the following figure has a radius of 20 cm and moment of inertia 0⋅2 kg-m2. The string going over it is attached at one end to a vertical spring of spring constant 50 N/m fixed from below, and supports a 1 kg mass at the other end. The system is released from rest with the spring at its natural length. Find the speed of the block when it has descended through 10 cm. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Four bodies of masses 2 kg, 3 kg, 4 kg and 5 kg are placed at points A, B, C, and D respectively of a square ABCD of side 1 metre. The radius of gyration of the system about an axis passing through A and perpendicular to plane is
From a circular ring of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
From a circular ring of mass ‘M’ and radius ‘R’ an arc corresponding to a 90° sector is removed. The moment of inertia of the remaining part of the ring about an axis passing through the centre of the ring and perpendicular to the plane of the ring is ‘K’ times ‘MR2 ’. Then the value of ‘K’ is ______.
A thin circular plate of mass M and radius R has its density varying as ρ(r) = ρ0r with ρ0 as constant and r is the distance from its center. The moment of Inertia of the circular plate about an axis perpendicular to the plate and passing through its edge is I = a MR2. The value of the coefficient a is ______.
A cubical block of mass 6 kg and side 16.1 cm is placed on a frictionless horizontal surface. It is hit by a cue at the top to impart impulse in the horizontal direction. The minimum impulse imparted to topple the block must be greater than ______ kg m/s.
