Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
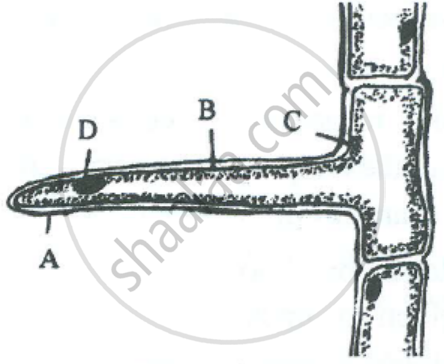
Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
उत्तर
|
Cell wall |
Cell membrane |
|
The cell wall of a root hair is freely permeable and allows both salt and water to pass through. |
The cell membrane of a root hair is semi-permeable and does not allow large dissolved salt molecules to pass through. |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Draw a magnified view of the root-hair, and describe, how it helps in the absorption of water from the soil.
How is root hair adapted for the absorption of water from the soil?
Choose the correct answer:
An example of a selective permeable membrane is __________
The diagram given below represents the result of an experiment conducted on two freshly taken shoots of a green herbaceous plant. The lower ends dip in the water.
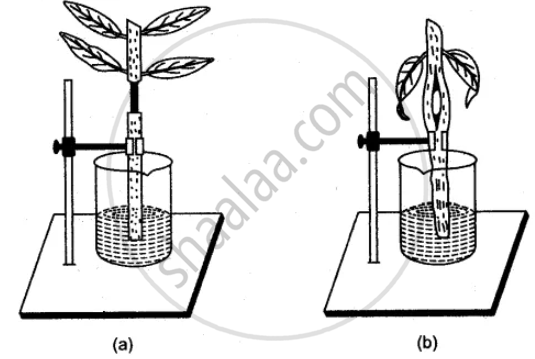
(i) What is the aim of the experiment?
(ii) Some parts of the stem in both the shoots have been removed. Name the conducting tissue in shoot A and in shoot B, that has been removed.
(iii) What are the results of this experiment?
Give Technical Term for the following.
Tissue which transports manufactured food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Identify the zone in wbkh root hair occurs.
Epiphytic plants like ____________ absorb water vapours from air with the help of epiphytic roots having special tissue called velamen.
How many regions are there in a typical root?
Epiphytic plants like orchids absorb water vapours from air with the help of ______ having special tissue called velamen.
Draw a neat and proportionate diagram of root hair and label mitochondria, nucleus and vacuole.
