Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
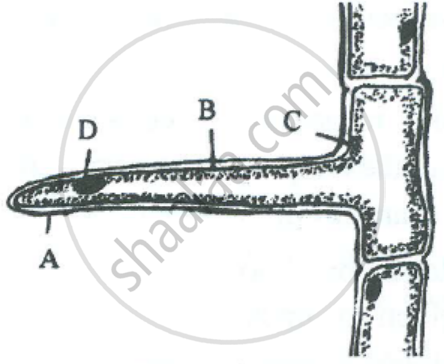
Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
Solution
|
Cell wall |
Cell membrane |
|
The cell wall of a root hair is freely permeable and allows both salt and water to pass through. |
The cell membrane of a root hair is semi-permeable and does not allow large dissolved salt molecules to pass through. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a magnified view of the root-hair, and describe, how it helps in the absorption of water from the soil.
Study the experimental setup in the figure and then answer the question that follow.
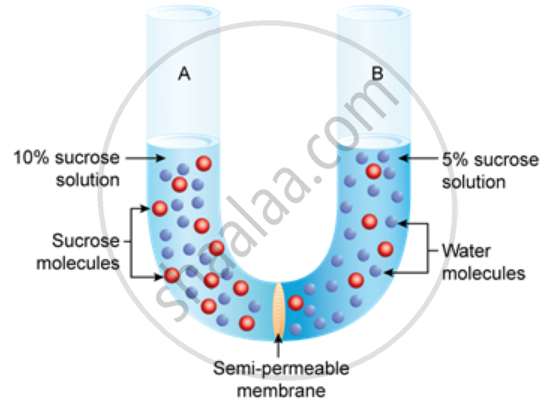
Explain the phenomenon mention in question 8.1 .
Differentiate between the following
Permeable and Semi-permeable membrane.
A thin strip of epidermal cells from the fleshy scales of an onion bulb was examined in a drop of water, under a microscope. All the epidermal cells looked alike and the figure alongside represents one of them. The thin strip was then transferred to a drop of strong sugar solution and re-examined under the microscope after about five minutes.

(i) Make a sketch of one of the epidermal cells, as it might appear after immersion in a strong sugar solution. Label any two parts which have undergone a change.
(ii) Give the scientific term for the change shown in Q.(i) above.
(iii) What would you do to bring this cell back to its original condition?
(iv) Give the scientific term used for the recovery of the cell as a result of the step taken in Q.(iii) above.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The tissue responsible for the ascent of sap in plants.
Name the following:
The solution outside the cell having lower solute concentration than the fluids.
Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the Root tip showing the root hair zone.
Epiphytic plants like ____________ absorb water vapours from air with the help of epiphytic roots having special tissue called velamen.
