Advertisements
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
▶ 4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 4 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 4 Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved Review Questions [Pages 52 - 55]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The hydrostatic pressure of the cell sap on the cell wall is called ______.
Turgor pressure
Osmotic pressure
Wall pressure
Atmospheric pressure
When a cell in solution shrinks and loses its shape, then the solution is ______.
Isotonic
Potable water
Hypotonic
Hypertonic
The process for which energy is required is ______.
Passive transport
Diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
The highest water potential (capacity to move out higher concentrated solution) is that of ______.
Pure water
10% salt solution
Honey
50% sugar solution
10% sugar solution
When the cells of a plant are fully distended, the condition is called ______.
Flaccidity
Shrinkage
Plasmolysis
Deplasmolysis
Which of the following creates a suction force in plants?
Transportation
Translocation
Transpiration
Transformation
The phenomenon by which living/dead plant cells absorb water by surface attraction is called ______.
Inhibition
Cohesion
Adhesion
Imbibition
Which of the following is a living, semi-permeable membrane?
Cell wall
Cell membrane
Cellulose
None
Addition of salt to pickles is a method of killing the bacteria by ______.
Imbibition
Diffusion
Deplasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Root pressure can be measured by using ______.
Sphygmomanometer
Barometer
Manometer
Thermometer
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name the following:
The condition of a cell placed in a hypotonic solution.
Name the following:
The process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets from leaf margins.
Name the following:
The process by which water enters root hairs.
Name the following:
The tissue concerned with upward conduction of water in plants.
Name the following:
The process by which molecules distribute themselves evenly within the space they occupy.
Name the following:
The pressure which is responsible for the movement of water molecules across the cortical cells of the root.
Give the equivalent term for the following:
Pressure exerted by the cell contents on the cell wall.
Give the equivalent term for the following:
The condition in which the cell contents are shrunken.
Give the equivalent terms for the following:
Loss of water through a cut stem.
Hypotonic solution is one in which the solution kept outside the cell has ______ solute concentration than inside the cell.
Active transport is one in which the ions outside the roots move in by utilising ______.
The bending movements of certain flowers towards the sun and the sleep movements of certain plants at night are examples of ______.
When placed in a more concentrated solution, the cell contents will ______.
shrink
swell up
The pressure by which the ______ molecules tend to cross the semi-permeable membrane is called osmotic pressure.
salt
water
Active transport is in a direction ______ to that of diffusion.
opposite
same
Match the items in column I with those in column II
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Xylem | (i) | semi - permeable |
| (b) | Phloem | (ii) | permeable |
| (c) | Cell membrane | (iii) | downward flow of sap |
| (d) | Root pressure | (iv) | upward flow of water |
| (e) | Cell wall | (v) | guttation |
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Differentiate between the following:
Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis.
Differentiate between the following:
Turgor pressure and wall pressure
Distinguish between the following:
Hypotonic and Hypertonic solutions
Differentiate between the following:
Turgidity and Flaccidity
Mention whether the following statement is true or false. Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
Addition of salt to pickles prevents growth of bacteria because they turn turgid.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true or false Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
Cells that have lost their water content are said to be deplasmolysed.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true or false. Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
Xylem is the water conducting tissue in plants.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true or false. Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
The shrinkage of protoplasm, when a cell is kept in hypotonic solution.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true or false. Correct the false statement by altering the last word only.
The cell wall of the root cell is a differentially permeable membrane.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Guttation is another name for bleeding in plants.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Soaked seeds burst into three seed coats.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
If the phloem of a twig is removed keeping the xylem intact, the leaves of a twig wilt.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Guttation in plants occurs maximum at midday.
True
False
Mention whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F) and give an explanation in support of your answer.
Raisins, when submerged in water, swell up due to endosmosis.
True
False.
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Give two examples of turgor movements in plants.
Define the following term:
Imbibition
Define diffusion.
Define the term Osmosis.
Define the following term:
Osmotic Pressure
Define the following term:
Active transport
Define the following term:
Tonicity
Give reasons for the following:
If you sprinkle some common salt on grass growing on a lawn, it is killed at that spot.
Give reason for the following:
If you uproot a plant from the soil, its leaves soon wilt.
Give reason for the following:
It is better to transplant seedlings in a flower-bed in the evening and not in the morning.
Give reason for the following:
A plant cell, when kept in a hypertonic salt solution for about 30 minutes, turns flaccid.
Give reason for the following:
Potato cubes, when placed in water, become firm and increase in size.
What are the four main forces which contribute to the ascent of sap (upward movement of water and minerals) ? Name them and explain in short.
What is transpirational pull?
How is transpirational pull caused?
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
A leaf cell of a water plant was placed in a liquid other than pond water. After sometime, it assumed a shape as shown below:
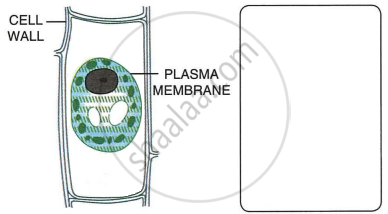
- Give the term for the state of the cell it has acquired.
- Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
- Comment on the nature (tonicity) of the liquid surrounding the cell.
- Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in an animal cell.
- Redraw in the space provided, the diagram of the cell if it is soon placed in ordinary water for some time.
The diagram given below represents an experimental set-up to demonstrate a certain process. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
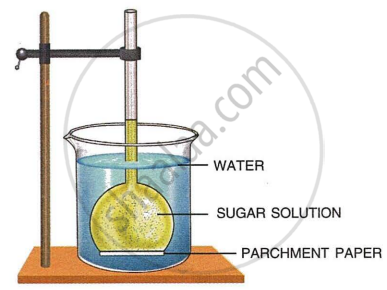
- Name the process.
- Define the above-named process.
- What would you observe in the experimental set-up after an hour or so?
- What control experiment can be set up for comparison?
- Keeping in mind the root hair, cell and its surroundings, name the parts that correspond to
- concentrated sugar solution
- parchment paper
- water in the beaker
- Name any other material that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment.
- Mention two advantages of the process for the plants.
The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
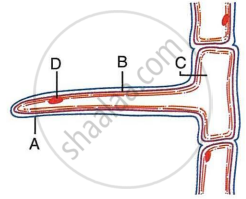
- Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
- The root hair cell is in a turgid state. Name and explain the process that caused this state.
- Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
- Draw a diagram of the above root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertiliser is added near it.
Study the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
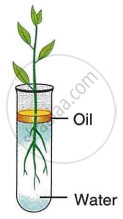
- Name the process being studied in the above experiment.
- Explain the process mentioned in (a) above
- Why is oil placed over water?
- What do we observe with regard to the level of water when this set-up is placed in (1) bright sunlight, (2) humid conditions and (3) windy days?
- Mention any three adaptations found in plants to foster the process mentioned in (a) above
Three cylinders of potato were carefully dried on blotting paper and weighed. Each piece weighed 3 grams. Each one was placed in the beaker as shown below:
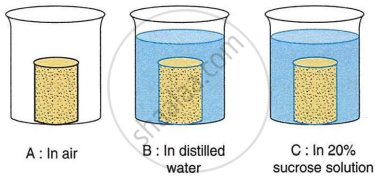
Answer the following questions:
- After 48 hours, which potato cylinder would be the heaviest?
- The movement of which substance is mainly responsible for the weight change in the potato cylinders?
- Name and define the process which is responsible for the movement of the substance mentioned in answer (b).
- Write specific names of the processes which occur in beakers B and C. [kinds of processes defined in answer (c)].
- Would there be any difference in the weight of the potato cylinder in beaker A after 48 hours? Give reason.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
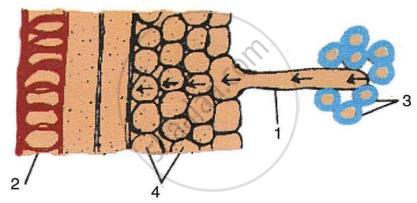
- The parts labelled as 1, 2, 3 and 4 are:
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Cortex respectively.
- Xylem vessel, Soil particles, Root hair, Cortex respectively.
- Root hair, Xylem vessel, Cortex, Soil particles respectively.
- Cortex, Soil particles, Xylem vessel, Root hair respectively.
- The process that enables the passage of water from soil into the root hair is:
- Diffusion
- Active transport
- Osmosis
- Passive absorption
- The kind of force which exists between a liquid and any surface is called as:
- Cohesive force
- Adhesive force
- Capillarity
- Suction force
- The kind of force between the same kind of liquid molecules is:
- Capillary force
- Transpirational pull
- Adhesive force
- Cohesive force
- Sometimes exudation of water occurs from the margin of the leaves in the early morning or night. It is termed as:
- Transpiration
- Guttation
- Bleeding
- Osmosis
Study the experimental setup in the figure and then answer the questions that follow.
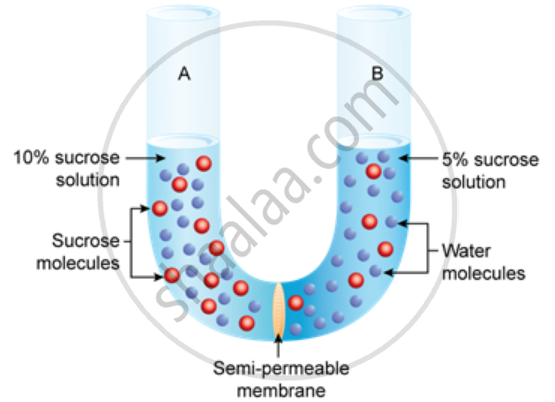
- What phenomenon is being studied by this setup?
- Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (a) above.
- What is meant by 'semipermeable membrane'?
- What will you observe in the set-up after about half an hour? Give a reason for your answer.
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
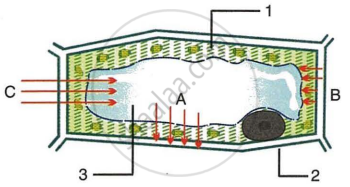
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
Solutions for 4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 - Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 4 (Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 4 Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved are Plant Anatomy and Plant Physiology, Characteristics of Roots for Absorbing Water, Concept of Osmosis, Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane), Concept of Imbibition, Simple Diffusion, Osmotic Pressure, Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis), Root Pressure, Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap), Water absorbing organ, Need of Water and Minerals for Plant, Active Transport, Means of Transport in Plants, Plant Anatomy and Plant Physiology, Characteristics of Roots for Absorbing Water, Concept of Osmosis, Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane), Concept of Imbibition, Simple Diffusion, Osmotic Pressure, Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis), Root Pressure, Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap), Water absorbing organ, Need of Water and Minerals for Plant, Active Transport, Means of Transport in Plants.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 4, Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
