Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
▶ 3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 3 Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals Review Questions [Pages 35 - 37]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
Which one of the following is the phenotypic monohybrid ratio in F2 generation?
3 : 1
1 : 2 : 1
2 : 2
1 : 3
If a pure tall plant is crossed with a pure dwarf plant, then offspring will be ______.
all tall
all dwarf
3 tall 1 dwarf
50% tall 50% dwarf
The 9 : 3 : 3 : 1 dihybrid ratio is due to ______.
segregation
crossing over
independent assortment
homologous pairing
A plant with green pods and smooth seeds with the genotype Ggss will give rise to the following gametes:
Gg and Ss
Gs and ss
Gs and gs
Gg and gs
The disease colour blindness is a ______.
Recessive X-linked disease
Dominant Y-linked disease
Recessive Y-linked disease
Dominant X-linked disease
The physical expression of a character is called ______.
Genotype
Alleles
Phenotype
Traits
Purity of gametes is linked to ______.
Law of dominance
Law of independent assortment
Law of segregation
Law of limiting factor
The phenotypic dihybrid ratio of F2 generation is ______.
9 : 3 : 1 : 1
9 : 1 : 3 : 1
9 : 1 : 3 : 3
9 : 3 : 3 : 1
In the human male, a sperm contains autosomes and ______.
X and Y chromosomes
Only X chromosome
X or Y chromosome
Only Y chromosome
If the mother is normal and the father is haemophilic, then their two daughters will be ______.
Normal
Haemophilic
Carrier
None
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE.
Match the terms in column I with their explanations in column II.
| Column I (Term) | Column I (Explanation) | ||
| a | genetics | 1 | Chromosomes similar in size and shape |
| b | Autosomes | 2 | The alternative forms of a gene |
| c | Recessive gene | 3 | Study of laws of inheritance of characters |
| d | Allele | 4 | A gene that can express only when in a similar pair |
| e | Homologous chromosomes | 5 | Chromosomes other than the pair of sex chromosomes |
Name any two genetic diseases in humans.
Which one of the following genotypes is homozygous dominant and which one homozygous recessive in regards to tongue rolling:
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Rewrite the correct form of the statement by changing the first or last word only:
Duplicated chromosomes remain attached at a point termed as centrosome.
Rewrite the correct form of the statement by changing the first or last word only:
The full complement of DNA of an organism is termed as genetics.
Rewrite the correct form of the statement by changing the first or last word only:
The inheritable feature of an organism is termed as heredity.
Rewrite the correct form of the statement by changing the first or last word only:
Terminal flower position is a dominant trait of pea flower.
Rewrite the correct form of the statement by changing the first or last word only:
Alternative forms of a gene are called traits.
Among lion, tiger and domestic cat, all three have the same number of 38 chromosomes, yet they have different appearances. How do you account for such differences ?
List any three features of garden pea with their dominant and recessive traits.
Explain why generally only the male child suffers from colour blindness and not the female?
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Define the following term:
Pedigree chart
Define the following term:
Variations
Define the term Mutation.
State the three Mendel’s laws of inheritance.
Does the sex of the child depend on the father or it is just a matter of chance? Discuss.
Distinguish between the following pair:
Karyotype and Karyokinesis
Distinguish between the following pair:
Autosomes and Sex chromosomes
Distinguish between the following pair:
Homozygous and Heterozygous chromosomes
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION AND SKILL TYPE
In a certain species of animals, black fur (B) is dominant over brown fur (b) Predict the genotype and phenotype of the offspring when both parents are ‘Bb’ or have heterozygous
black fur .
Two pairs (A & B) of rabbits were crossed, as given below:
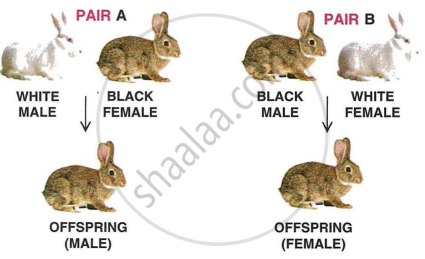
- Can you tell which coat colour (black or white) is dominant?
- Is the coat colour sex-linked?
Make a Punnett square and find out the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of F2 generation in the progeny of a genetic cross between:
- A pure tall (TT) pea plant with a pure dwarf (tt) pea plant.
- Red flower variety of pea (RR) with white flower variety of pea (rr).
Mendel crossed a homozygous pea plant having round seeds (RR) with a homozygous pea plant having wrinkled seeds (rr). He got different results. On the basis of it, answer the following questions:
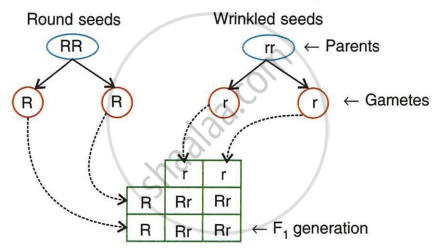
- Which character of seed is studied in the experiment?
- Which of the above two traits is dominant?
- Write the phenotype and genotype of F1 offspring.
- Mention and state Mendel's law as shown in the above cross.
- Make a Punnett square for F2 generation when two plants of F1 offspring are crossed with each other.
- Write the phenotypic ratio of F2 progeny.
- What will be the genotypic ratio of F2 offspring?
- What are the two traits of seed colour ? Also mention which is dominant and recessive?
- Write the scientific name of the garden pea.
- Write two main features of the pea plant, due to which Mendel selected it for his hybridisation studies.
A homozygous plant having round (R) and yellow (Y) seeds is crossed with another homozygous plant having wrinkled (r) and green (y) seeds. Answer the following questions:
- Give the genotype of the F1 generation.
- Mention the phenotype of the F1 offspring.
- Give the possible combinations of gametes that can be obtained from F1 hybrids.
- Give the dihybrid phenotypic ratio and the phenotype of the offspring of the F2 generation when two plants of F1 generation are crossed.
- Name and state the law which explains the dihybrid phenotypic ratio.
Solutions for 3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 - Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 3 (Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 3 Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals are Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics, Heredity or Inheritance, Variation, Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity, Types of Chromosomes, Mendel's Experiments Inheritance, Mutation, Genes and Genetic, Monohybrid Cross, Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics, Sex Determination, Sex Linked Inheritance, Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity, Genes and their Alleles, Genotype and Phenotype, From parents to children - tongue rolling - An example of inheritance, Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics, Heredity or Inheritance, Variation, Chromosomes - The Carriers of Heredity, Types of Chromosomes, Mendel's Experiments Inheritance, Mutation, Genes and Genetic, Monohybrid Cross, Gregor Johann Mendel – Father of Genetics, Sex Determination, Sex Linked Inheritance, Mendelian Inheritance - Mendel’s Law of Heredity, Genes and their Alleles, Genotype and Phenotype, From parents to children - tongue rolling - An example of inheritance.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
