Advertisements
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
▶ 5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Transpiration Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Transpiration - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 5: Transpiration
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 5 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 5 Transpiration Review Questions [Pages 66 - 68]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The process of evaporative loss of water from the aerial parts of a plant is ______.
Ascent of sap
Translocation
Transpiration
Exudation
The process of oozing out of the fluids from a plant part is ______.
Transpiration
Excretion
Transportation
Exudation
Transpiration occurs:
More from the adaxial surface of a monocot leaf
More from the adaxial surface of a dicot leaf
Equal from both the surfaces of a dicot leaf
More from the abaxial surface of a dicot leaf
Guttation takes place through:
Stomata
Lenticels
Lower epidermis of leaves
Hydathodes
Cuticle
The apparatus used to measure the rate of transpiration is ______.
Barometer
Clinostat
Manometer
Potometer
Which of the following is an external factor affecting the rate of transpiration?
Number of stomata
Exposed surface
Humidity
Sunken stomata
The upper layer of mesophyll in a leaf consists of elongated ground tissue called ______.
Spongy parenchyma
Palisade cells
Xylem cells
Phloem cells
Transpiration is significant for all except ______.
Cooling effect
Suction pull
Ascent of sap
Translocation of food
Hydathodes are located on ______.
At the petiole
Upper surface of leaves
Lower surface of leaves
Margins of leaves
When guard cells are flaccid, the stoma must be ______.
Open
Neither open nor closed
Closed
None of these
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name the following:
openings on the stem through which transpiration occurs.
Name the following:
The process by which the intact plant loses water in the form of droplets.
Name the following:
An instrument used to find the rate of transpiration.
Name the following:
A plant in which the stomata are sunken
Name the following:
The apparatus to record the rate of transpiration in a cut shoot.
Name the following:
Any two parts of a leaf which allow transpiration.
Name the following:
The structure in a leaf that allows guttation.
Name the following:
Loss of water as droplets from the margins of certain leaves.
Transpiration is the loss of water as water ______ from the ______ parts of the plant.
Closing of ______ and shedding of leaves reduce ______.
Transpiration helps in creating ______ force and in eliminating excess ______.
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis
In a similar way, write the functional activity against the following:
Hydathodes and ______
Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
Chloroplasts and photosynthesis
In a similar way, write the functional activity against the following:
Leaf spines and ______
Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
Chloroplasts and Photosynthesis
In a similar way, write the functional activity against the following:
Lenticels and ______
Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
chloroplasts and photosynthesis
In a similar way, write the functional activity against the following:
Xylem and ______
(a) State whether the following statement are True or False.
(b) Rewrite the false statement in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Most transpiration occurs at midnight.
True
False
(a) State whether the following statement are True or False.
(b) Rewrite the false statement in (a) above in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Transpiration creates a pull for the upward movement of the sap.
True
False
(a) State whether the following statement are True (T) or False (F)
(b) Rewrite the false statement in (a) above in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Wind velocity has an effect on transpiration.
True
False
(a) State whether the following statement are True or False.
(b) Rewrite the false statement in (a) above in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Atmospheric humidity promotes transpiration from a green plant.
True
False
(a) State whether the following statement are True or False.
(b) Rewrite the false statement in the correct form by changing either the first or the last word only.
Transpiration helps to cool the body of the plant.
True
False
Match the terms given in column A with column B:
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (a) | Hydathodes | (i) | Photosynthesis |
| (b) | Stomata | (ii) | Respiration |
| (c) | Cuticle | (iii) | Regulates opening and closing of stomata |
| (d) | Lenticels | (iv) | Reduces loss of water |
| (e) | Guard cells | (v) | Guttation |
Name the three kinds of transpiration.
Name the three external factors which increase the rate of transpiration.
Name the three intrinsic features which reduce the rate of transpiration.
Name three extrinsic factors which decrease the rate of transpiration.
Name four kinds of potometers on the basis of the names of the scientists who discovered them.
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Define the following Term:
Transpiration
Define the following term:
Exudation
Define the following term:
Potometer
Define the following term:
Wilting
Define the following term:
Hydathodes
Define the following term:
Cuticle
Distinguish between the following:
Stomata and lenticels
Differentiate between guttation and bleeding in plants.
Distinguish between the following:
Transpiration and evaporation
Give a reason/suitable explanation.
Nerium loses less amount of water during transpiration.
Give a reason/suitable explanation.
More transpiration occurs from the under surface of a dicot leaf.
Give a reason/suitable explanation.
Transpiration increases with the velocity of the wind.
Give a reason/suitable explanation.
Leaves of some plants wilt during midday and recover in the evening.
Give a reason/suitable explanation.
Guttation normally occurs during early mornings or late nights.
Give a reason/suitable explanation.
Forests tend to bring more rains.
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
The given figure represents an experiment:
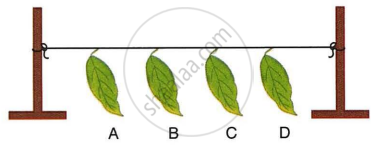
- Leaf A was coated with grease on both surfaces.
- Leaf B was coated with grease on the lower surface.
- Leaf C was coated with grease on the upper surface.
- Leaf D was left without any application of grease. All four leaves A, B, C and D were left in a room for about 24 hours.
- Which leaf dries first? Give reason.
- Which leaf dries last? Give reason.
Given below is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:

- Name the apparatus.
- What is it used for?
- What is the role played by the air-bubble in this experiment?
- What is the use of the reservoir?
- What happens to the movement of the air-bubble if the apparatus is kept:
- in the dark
- in sunlight
- in front of a fan?
Give a reason in each case.
Given ahead is a diagram of an experimental setup to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:

- Name the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper.
- Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
- Why are glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
- After about half an hour, what change, if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper placed on the dorsal and ventral sides of the leaf? Give a reason to support your answer.
An outline sketch of a tree is shown in a diagram below. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
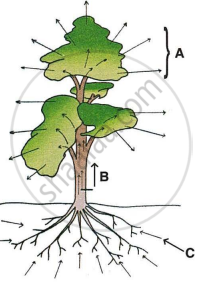
- Name and define the phenomenon labelled A in the diagram.
- Write the significance of the process mentioned in A for the plants.
- What do the direction of the arrows in B and C indicate? Name the phenomena.
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of an opened stomata.
The figure given below represents an experimental setup with a weighing machine to demonstrate a particular process in plants. The experimental set-up was placed in bright sunlight. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
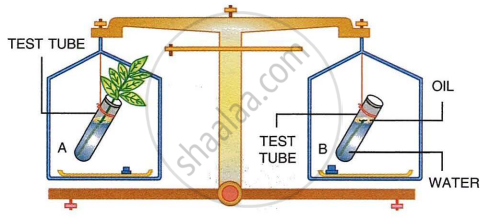
- Name the process intended for the study.
- Define the above mentioned process.
- When the weight of the test tubes (A and B) is taken before and after the experiment, what is observed? Give reasons to justify your observations in A & B.
- What is the purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental set-up?
- What is the purpose of putting oil in the test tube?
An apparatus, as shown below, was set up to investigate a physiological process in plants. The setup was kept in sunlight for two hours. Droplets of water were then seen inside the bell jar. Answer the questions that follow:

- Name the process being studied.
- Explain the process named above in Q.3(a)(i).
- Why was the pot covered with a plastic sheet?
- Suggest a suitable control for this experiment.
- Mention two ways in which this process is beneficial to plants.
- List three adaptations in plants to reduce the above mentioned process.
Given below is the figure of a stoma. Study the same and answer the following questions:
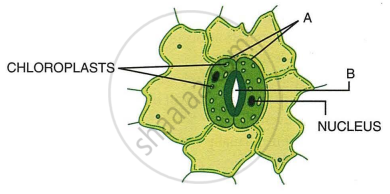
- Label the guidelines A and B.
- Write the exact location of the above-mentioned structures.
- Mention one important role of structure A.
- Write three important roles for structure B.
- Redraw the same figure when structures A are in flaccid condition. When does the flaccid condition occur?
Solutions for 5: Transpiration
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Transpiration Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Transpiration - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 - Transpiration
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 5 (Transpiration) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 5 Transpiration are Transpiration, Measurement of Transpiration, Types of Transpiration, Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration, Adaptations in Plants to Reduce Excessive Transpiration, Significance of Transpiration, Direct Loss of Water by Plants - Guttation and Bleeding, Transpiration, Measurement of Transpiration, Types of Transpiration, Factors Affecting the Rate of Transpiration, Adaptations in Plants to Reduce Excessive Transpiration, Significance of Transpiration, Direct Loss of Water by Plants - Guttation and Bleeding.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Transpiration exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 5, Transpiration Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
