Advertisements
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
▶ 8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - The Circulatory System Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - The Circulatory System - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 8: The Circulatory System
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 8 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 8 The Circulatory System Progress Check [Pages 94 - 110]
Name the two fluids that circulate in the body.
In a coloured diagram, why do we generally show the pulmonary artery in blue and pulmonary vein in red colour?
Name any four substances transported by blood.
Name the following:
The yellow coloured fluid part of the blood .
Name the following:
The respiratory pigment contained in RBCs.
Name the following:
Any two organelles absent in mature RBCs.
Name the following:
The process of WBCs squeezing out through the walls of the blood capillaries.
Mention the following:
Average life span of RBCs.
Mention the following:
Range of RBCs per mm3 in a normal adult human female.
Mention the following:
The two major categories of WBCs.
Mention the following:
Blood cells involved in leukaemia.
State whether the following statement is true or false and correct the false statement.
Process of coagulation starts with the release of a substance from RBCs.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false and correct the false statement.
Blood fails to clot readily in the case of deficiency of calcium.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false and correct the false statement.
The solid fibrin and thrombin are one and the same thing.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true or false and correct the false statement.
The clear liquid that oozes out after the formation of a clot is serum.
True
False
Name the following:
The category of vitamin required for clotting of blood.
Name the following:
Any two diseases related with blood clotting.
Name the following:
The antibodies present in the plasma of O type blood group.
Name the following:
The animal for which Rh stands in the context of blood group.
Ventricles have ______ walls when compared with those of auricles.
Ventricles give rise to two large blood vessels called ______ and ______.
The exact location of the tricuspid valve
Where is the following located?
Mitral valve
Mention the exact location of the Pulmonary semilunar valve
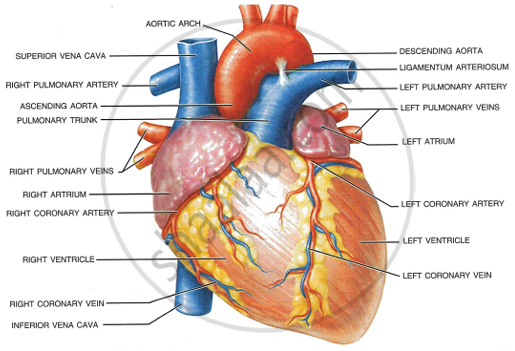 |
Can you answer why the pulmonary artery shown in Fig. is blue in colour?
Name the following:
Contraction phase of heart.
Name the following:
The structure that holds the heart valves in position.
Mention the phase of heart beat in which both the atrio-ventricular valves are closed.
Fill in the blanks
The ______ have thin and less muscular ______ and have ______ to prevent back flow of ______.
______ carry blood to an organ and break up into ______ ending in capillaries.
Walls of capillaries consist of a single layer of squamous ______ cells.
The substances to and from the tissues diffuse through the walls of ______.
Name the two major circulations of blood in the human body.
From where to where do the following blood vessel carry blood?
Pulmonary artery
From where to where do the following blood vessel carry blood?
Renal artery
From where to where do the following blood vessel carry blood?
Posterior vena cava
From where to where do the following blood vessel carry blood?
Hepatic vein
From where to where do the following blood vessel carry blood?
Hepatic portal vein
Define portal vein.
What is pulse?
What are the normal values of blood pressure in a normal human adult?
Which kind of cells are found in the lymph?
Give the functions of lymph.
Name the two main lymphatic organs in humans.
Name the following:
The smallest W.B.C.
Name the following:
Part of lymphatic system concerned with absorption of fats from the intestine.
Name the following:
A special lymphatic node on the sides of the neck.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 8 The Circulatory System Review Questions [Pages 111 - 113]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE (Select the most appropriate option in each case)
The corpuscles which transport the respiratory gas oxygen to the different parts of the body ______.
Leukocytes
Thrombocytes
Erythrocytes
Lymphocytes
Which of following acts like a blood reservoir?
Tonsils
Lymph
Spleen
Tissue fluid
The process of engulfing bacteria by Neutrophils is called ______.
Diapedesis
Diuresis
Phagocytosis
Diastole
The artery with the highest amount of nitrogenous wastes is ______.
Hepatic artery
Renal artery
Pulmonary artery
Coronary artery
The compound formed by the combination of haemoglobin and carbon dioxide is ______.
Carbaminohaemoglobin
Carboxyhaemoglobin
Oxyhaemoglobin
Carbogen
Which of the following chemical substances is released from Eosinophils?
Histones
Antitoxins
Antibodies
Histamine
The doubled-layered membrane which covers and protects the heart is ______.
Pericardia! fluid
Meninges
Pericardium
Pleura
The blood vessel without a mascular layer in its wall ______.
Capillary
Vein
Artery
Portal vein
The blood vessel which carries blood from the stomach and intestine to the liver:
Hepatic artery
Carotid artery
Hepatic vein
Hepatic portal vein
The kind of cells that initiate blood coagulation:
Monocytes
Lymphocytes
Leukocytes
Thrombocytes
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Given below is a certain structure, write its chief functional activity.
Blood platelets - ______.
Given below is a certain structure, write its chief functional activity.
Neutrophils - ______.
Given below is a certain structure, write its chief functional activity.
Erythrocytes - ______.
Given below is a certain structure, write its chief functional activity.
Lymphocytes - ______.
Given below is a certain structure, write its chief functional activity.
Bone marrow - ______.
Name these:
Three components of circulatory system.
Name these:
Three kinds of blood cells.
Name these:
Three kinds of blood vessels.
Name these:
Three circulating fluids in human body.
Name these:
Three non-circulating fluids in human body
Name the two main lymphatic organs in humans.
Name the following:
Components of blood
Name these:
Two kinds of circulatory systems in different animals.
Name these:
Two components of haemoglobin.
Name these:
Two phases of circulation of blood in human body
Name the following:
Any one vein which starts from an organ and ends in another organ besides the heart
Name the following:
The kind of blood vessels which have no muscular walls
Name the following:
The artery which carries deoxygenated blood.
Name the following:
The kind of blood cells which can squeeze out through the walls of one category of blood vessels.
Name the following:
The smallest common blood vessels formed by the union of capillaries.
Name the following:
The blood vessel which starts from capillaries and ends in capillaries.
Name the following:
The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the auricles contract.
Name the following:
The valve present in between the chambers on the right side of the human heart.
Name the following:
The phase of the cardiac cycle in which the ventricles get filled with blood from the atrium.
Name the following:
The fluid found between the membranes of the heart.
Complete the following statements by filling in the blanks from the choices given in the options.
The blood vessel that begins and ends in capillaries is the ______.
Hepatic artery
Hepatic portal vein
Hepatic vein
A blood vessel which has small lumen and thick wall is ______.
Capillary
Lymphatic duct
Artery
Venule
The valve which prevents back flow of blood in the veins and lymph vessels is ______.
Mitral valve
Tricuspid valve
Pocket-shaped valve
An anticoagulant present in the blood is ______.
Heparin
Hirudin
Thromboplastin
Calcium
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest a suitable word/words for the fourth place:
Lub : Atrioventricular valves :: Dup : ______
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest a suitable word/words for the fourth place:
Coronary artery : Heart :: Hepatic artery : ______
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest a suitable word/words for the fourth place:
RBCs: Polycythernia :: WBCs. : ______
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest a suitable word/words for the fourth place:
WBCs : ______ :: RBCs : Erythropenia
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest a suitable word/words for the fourth place:
Chest pain : Angina pectoris :: Heart attack : ______
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Enumerate the structural differences between white blood cells and red blood cells.
When are the sounds "LUBB" and "DUP" produced respectively during heart beat?
Match the items in Column ‘A’ with those in column ‘B’ Rewrite the correct matching pairs.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (a) | SA Node | (i) | Plasma |
| (b) | Defective haemoglobin in RBC | (ii) | Serum |
| (c) | Muscle fibres located in heart | (iii) | Pacemaker |
| (d) | The liquid squeezed out of blood during clotting | (iv) | Sickle cell anaemia |
| (e) | Never tires, keep on contracting and relaxing | (v) | Purkinje fibres |
| (f) | Cardiac cycle | (vi) | Cardiac muscle |
| (g) | Liquid part of the blood without corpuscles | (vii) | 0·85 sec |
The table below is designed to indicate the transport of certain substances in our body. Fill in the blanks with suitable answers.
| Substance | From | To | |
| 1. | ______ | Lungs | Whole Body |
| 2. | Carbon Dioxide | ______ | ______ |
| 3. | Urea | ______ | ______ |
| 4. | Digested Carbohydrates | Intestines | ______ |
| 5. | ______ | ______ | Target Organs |
| 6. | Heat | ______ | Whole Body |
Define the Circulatory system.
Define the following term:
Blood
Define the following term:
Heart
Define the following term:
Diapedesis
Define the following term:
Phagocytosis
Define the following term:
Rh factor
Distinguish between the following pair on the basis of words indicated in the bracket ( ):
Erythrocytes and Leukocytes (Nucleus)
Distinguish between the following pair on the basis of words indicated in the bracket ( ):
Leukocytes and Thrombocytes (Life-span)
Distinguish between the following pair on the basis of words indicated in the bracket ( ):
Arteries and Veins (Wall and lumen)
Distinguish between the following pair on the basis of words indicated in the bracket ( ):
Pulmonary and Systemic circulation (Kind of blood)
Distinguish between the following pair on the basis of words indicated in the bracket ( ):
Mitra! valve and Tricuspid valve (Location)
Give biological reasons for the following statements:
The left ventricle of the heart has a thicker wall than the right ventricle.
How do you account for the following difference?
The walls of the right ventricle are thicker than those of the right auricle.
Give reasons/explain:
Vitamin K is essential for the process of blood clotting.
Give reasons/explain:
A mature mammalian Erythrocyte lacks nucleus, mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
Why do people have a common belief that the heart is located on the left side of the chest?
What is the function of tonsils?
What is the function of spleen?
Write important role/roles of the following:
Hepatic portal vein
Write important role/roles of the following:
Hepatic portal vein
Write important role/roles of the following:
S.A.N.
What is meant by the term 'Double circulation'?
What is the difference between pulmonary circulation and systemic circulation?
Write the main steps in coagulation of blood in their correct sequence?
Mention the exact location of the Pulmonary semilunar valve
State the Location:
Tonsils
Write the exact location of the following:
Heart
Write the exact location of the following:
Pacemaker
Write the exact location of the following:
Hepatic portal vein
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
Given alongside is a diagram of a smear of human blood. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
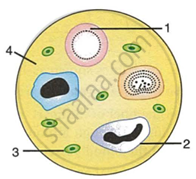 |
- Name the parts l, 2, 3 and 4 indicated by guidelines.
- Mention two structural differences between the parts labelled 'l' and '2'.
- What is the main function of the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3 respectively?
- What is the life span of the part labelled '1'?
- Name a soluble protein found in '4' which helps in the clotting of blood.
Given below is a highly schematic diagram of the human blood circulatory system.
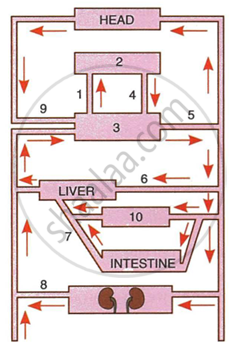 |
- Which part (state the number) represents the heart? Give reason in support of your answer.
- Which numbers represent the following, respectively?
Aorta Superior vena cava Hepatic portal vein Renal Vein Pulmonary artery Stomach
The figures given below show diagrammatic cross sections of three kinds of blood vessels.
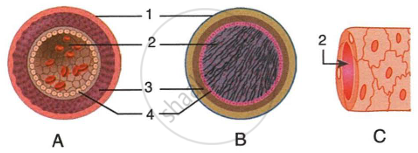 |
- Identify the blood vessels A, B and C.
- Name the parts labelled 1-4.
- Mention two structural differences between A and B.
- Name the kinds of blood that flow through A and through B respectively.
- In which one of the vessels referred to in (a) above does the exchange of gases actually take place?
The diagram given below represents the human heart in one phase of its activity. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
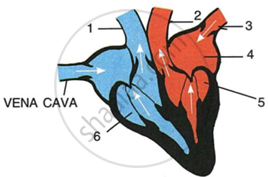 |
- Name the phase.
- Which part of the heart is contracting in this phase? Give a reason to support your answer.
- Name the parts numbered 1to6.
- What type of blood flows through the parts marked 'l' and '2' respectively?
- How many valves are closed in this phase?
Study the following diagram carefully and then answer the questions that follow:
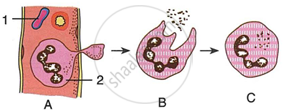 |
- Name the cell labelled 1.
- Identify the phenomenon occurring in A.
- Mention two structural differences between 1 and 2.
- Name the process occurring in B and C and state the importance of this process in the human body.
Given diagram is a schematic representation of the circulatory system in humans. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
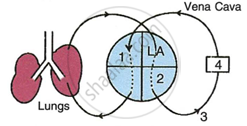 |
- Label the parts 1 and 4 indicated in the diagram.
- Which of the above mentioned number is the thickest artery? Also write its name.
- Mention the number and chamber of the heart which has the thickest muscular wall.
- Which of the above numbers/structures has the maximum number of blood capillaries?
- Draw neat and labelled diagrams of the transverse section of vena cava and the part numbered as 3. Make sure to show the structural differences between these two in the diagram.
Given alongside are diagrams of a certain category of blood vessels showing the role of a special structure in their walls. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow.
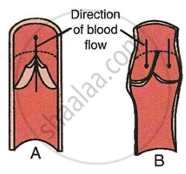 |
- Name the kind of blood vessels shown in the figure. What are its branches termed as?
- Name the structure shown inside the blood vessels. Write its important role.
- What kind of blood flows through these blood vessels normally? Name the blood vessel which carries blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Name a similar kind of blood vessel which is related to the liver and kidney.
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the transverse section of the blood vessel shown above showing the three layers of its wall and lumen.
Given below is a diagram of the external features of the human heart. Study the figure and answer the questions that follows:
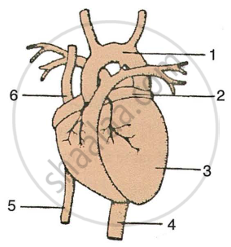 |
- Label the guidelines shown as 1 to 6 in the figure.
- Write the important role of parts 5 and 6.
- Name the chamber of the heart which collects blood from the lungs through a blood vessel. Also write the name of the blood vessel.
- Write one structural and one functional difference between the blood vessels 4 and 5.
- What happens when there is a blockage in any coronary artery or any of their branches?
Solutions for 8: The Circulatory System
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - The Circulatory System Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - The Circulatory System - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 - The Circulatory System
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 8 (The Circulatory System) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 8 The Circulatory System are Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes), Blood Circulatory System in Human, Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart), Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation), Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system), Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP", Working mechanism of human heart, Pacemaker, Blood Vessels, Blood Pressure (B.P.), Tissue Fluid (Or Intercellular Fluid), Lymph and Lymphatic System, The Spleen, Circulation in Animals, Fluids in Our Body, Blood, Functions of Blood, Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood), Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes), Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Human Heart, Types of Closed Circulation, Composition of Blood: Blood Platelets (Thrombocytes), Blood Circulatory System in Human, Circulation of Blood in the Heart (Functioning of Heart), Function of Platelets - Clotting of Blood (Coagulation), Blood Transfusion and Blood Groups (ABO and Rh system), Heart Beat - Heart Sounds "LUBB" and "DUP", Working mechanism of human heart, Pacemaker, Blood Vessels, Blood Pressure (B.P.), Tissue Fluid (Or Intercellular Fluid), Lymph and Lymphatic System, The Spleen, Circulation in Animals, Fluids in Our Body, Blood, Functions of Blood, Composition of Blood: Plasma (The Liquid Portion of Blood), Composition of Blood: Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes), Composition of Blood: White Blood Cells (Leukocytes), Human Heart, Types of Closed Circulation.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions The Circulatory System exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 8, The Circulatory System Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
