Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Given below is a diagram of the external features of the human heart. Study the figure and answer the questions that follows:
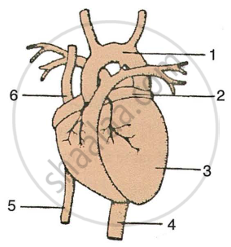 |
- Label the guidelines shown as 1 to 6 in the figure.
- Write the important role of parts 5 and 6.
- Name the chamber of the heart which collects blood from the lungs through a blood vessel. Also write the name of the blood vessel.
- Write one structural and one functional difference between the blood vessels 4 and 5.
- What happens when there is a blockage in any coronary artery or any of their branches?
Solution
-
- Aorta
- Left Atrium
- Left Ventricle
- Dorsal Aorta
- Inferior Vena Cava
- Superior Vena Cava
- The vena cava is a vein that transports deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart. There are two vena cava, superior and inferior. The superior vena cava transports deoxygenated blood from the upper body, including the head, arms, and neck. In contrast, the inferior vena cava transports it from the lower body, including the legs and abdominal organs.
- The left atrium receives blood from the lungs through pulmonary veins.
- The structural difference between the inferior vena cava and the dorsal aorta.
The inferior vena cava has valves and a broader lumen, while the dorsal aorta has no valves and a limited canal.
The functional distinction between the inferior Vena Cava and the dorsal aorta.
The dorsal aorta transports oxygenated blood from the heart's left ventricle to the body, while the vena cava drains deoxygenated blood to the right ventricle. - A coronary artery blockage or branch can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle. Reduced blood flow can cause chest pain (angina) and, in severe situations, heart attack (myocardial infarction) by damaging the heart muscle. The severity of the repercussions varies depending on the size of the blockage and impacted blood vessels.
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What are the functions of these components?
Choose the correct answer:
Which chamber of the heart has the thickest wall?
State the Function: Chordae tendinae
Column 2 is a list of items related to ideas in Column 1. Match the term in Column 2 with the suitable idea given in Column 1.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
| (i) Superior vena cava | (a) Collect deoxygenated blood from the wall of the heart. |
| (ii) Inferior vena cava | (b) Carry oxygenated blood to heart muscle. |
| (iii) Pulmonary vein | (c) Collects deoxygenated blood from upper part. |
| (iv) Coronary veins | (d) Collects deoxygenated blood from lower parts. |
| (v) Coronary artery | (e) Brings oxygenated blood from lungs. |
| (vi) Aorta | (f) Large artery |
| (vii) Heart attack | (g) Large vein |
| (viii) Blood Pressure | (h) Oxygenated blood |
| (ix) Tricuspid valve | (i) Sphygmomanometer |
| (x) Bicuspid valve | (j) Allows blood flow from right auricle to right ventricle. |
| (xi) Contraction and relaxation of heart | (k) Blocking of coronary arteries. |
| (l) Cardiac muscle. | |
| (m) Allows blood flow from left auricle to left ventricle. | |
| (n) Allows blood flow from right ventricle of pulmonary aorta. |
Draw diagram of conducting system of human heart. Label SA node and bundle of His.
The given diagram represents the conducting system of human heart. Identify 1, 2, 3, 4.
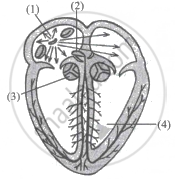
Left atrium : pulmonary vein : right ventricle : ____________.
The heart forms an effective barrier against infection by microbes and pathogens.
Heart sound 'dub' is caused due to closing of ______.
What is the role of Paplillary muscles?
