Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
▶ 10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - The Nervous System Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - The Nervous System - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 10: The Nervous System
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 10 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 The Nervous System Progress Check [Pages 129 - 137]
Name the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Write one word for the following:
wave of electrical disturbance that sweeps over the nerve cell.
Write one word for the following:
Long thread-like part of the nerve cell.
Write one word for the following:
Point of contact between two nerve cells.
Write one word for the following:
A bundle of axons enclosed in a tubular sheath.
Write one word for the following:
The kind of nerve carrying impulses from the brain to a gland or muscle.
Categorise the following under stimulus and response.
Withdrawal of hand on touching a hot plate
Categorise the following under stimulus and response.
Seeing a green light turning into red at a road crossing before applying the brakes.
Categorise the following under stimulus and response.
Pain in the eye if something falls into it.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the correct alternative given for each.
Brain and spinal cord are the parts of ______ nervous system.
Central
peripheral
autonomous
______ is the largest part of the brain.
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Cranial nerve
Spinal nerve
medulla oblongata
White matter consists mainly of ______.
axons
dendrites
cytons
The part of the brain concerned with body balance is ______.
cerebrum
cerebellum
medulla oblongata
Given below is a common reflex in humans. Classify it as a simple or conditioned reflex.
Knee-jerk
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
Given below is a common reflex in humans. Classify it as a simple or conditioned reflex.
Watering of mouth on seeing a favourite dish.
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
Given below is a common reflex in humans. Classify it as a simple or conditioned reflex.
Tying of shoe laces while talking.
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
Given below is a common reflex in humans. Classify it as a simple or conditioned reflex.
Closing of eyelids if a strong beam of light is flashed across.
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
Given alongside is a partial diagrammatic representation of a certain phenomenon pertaining to the nervous system.
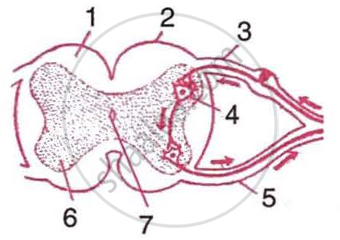 |
- Name the parts numbered 1-7.
- Name the phenomenon that the diagram depicts and define it.
- Give the technical term for the point of contact between two nerve cells.
- Name the parts not shown in the diagram that should be included to complete the pathway of the phenomenon.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 10 The Nervous System Review Questions [Pages 138 - 141]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE (Select the most appropriate option in each case).
The basic structural and functional unit of brain is ______.
Cyton
Nephron
Axon
Neuron
Which of the following structures is absent in nerve cells?
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Centrosome
Neurilemma
The number of cranial and spinal nerves in a human being are respectively ______.
31, 12 pairs
32, 21 pairs
12, 31 pairs
31, 21 pairs
Which part of the brain controls the posture of our body?
Cerebrum
Medulla oblongata
Cerebellum
Pons
The central cavity of the brain is termed as ______.
Thalamus
Ventricle
Hypothalamus
Auricle
Nissl's granules are found in the cytoplasm of ______.
Nerve cell
Dendrons
Axon
Dendrites
The thin delicate middle layer of meninges is termed as ______.
Choroid
Dura mater
Arachnoid
Pia mater
Any factor that can bring a change in the body of an organism is called ______.
Response
Stimulus
Reflex
Impulse
Gyri and sulci are richly found in ______.
Renal cortex
Cerebral cortex
Spinal cortex
Adrenal cortex
The white matter of cerebrum mainly consists of ______.
Cytons
Dendrons
Axons
Dendrites
VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Name the following:
The fluid that is present inside and outside the brain.
Name the following:
The junction between two nerve cells.
Name the following:
The part of the brain which is concerned with memory.
Name the following:
The central space of the brain.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Stimulus : Receptor :: Impulse : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Cerebrum : Diencephalon :: Cerebellum : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Receptor : Sensory nerve :: Motor nerve : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Axons : Nerve :: Cytons : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Cerebrum : Corpus callosum :: Cerebellum : ______.
Given below is a set of four terms. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining terms:
Duramater
Gray matter
Piamater
Arachnoid
Given below is a set of four terms. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining terms:
Cerebrum
Cerebellum
Spinal cord
Medulla oblongata
Given below is a set of four terms. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining terms:
Pons
Cyton
Axon
Dendrons
Given below is a set of four terms. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining terms:
Hypothalamus
Cerebellum
Pons
Medulla oblongata
Given below is a set of four terms. Choose the odd one and write the category of the remaining terms:
Sneezing
Blinking
Blushing
Knitting without looking
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Mention where in the human body is the following located and state its main function:
Corpus callosum
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F).
The main component of the white matter of the brain is perikaryon.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F).
The arachnoid layer fits closely inside the pia mater.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F).
A double chain of ganglia, one on each side of the nerve cord belongs to the spinal cord.
True
False
State whether the following statement is true (T) or false (F).
Dura mater is the outermost layer of the meninges.
True
False
State whether the following is simple reflex, conditioned reflex or neither of the two.
Sneezing
Simple reflexes
Conditioned reflexes
None of the above
State whether the following is simple reflex, conditioned reflex or neither of the two.
Blushing
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
None of the above
State whether the following is simple reflex, conditioned reflex or neither of the two.
Contraction of eye pupil
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
None of the above
Mention where in the human body is the following located and state its main function:
Central canal
State whether the following is simple reflex, conditioned reflex or neither of the two.
Lifting up a book
simple reflex
conditioned reflex
None of the above
State whether the following is simple reflex, conditioned reflex or neither of the two.
Knitting without looking
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
None of the above
State whether the following is simple reflex, conditioned reflex or neither of the two.
Sudden application of brakes of the cycle on sighting an obstacle in front
Simple reflex
Conditioned reflex
None of the above
Write the function of Association neuron.
State the Function:
Myelin sheath
Write the function of medullary sheath.
The main function of Cerebrospinal fluid.
Rearrange the following in correct sequence pertaining to what is given within brackets at the end.
Effector - Sensory neuron - Receptor - Motor neuron - Stimulus - Central nervous system Response (Reflex arc)
Rearrange the following in correct sequence pertaining to what is given within brackets at the end.
Repolarisation - Depolarisation - Resting (polarised) (during conduction of nerve impulse through a nerve fibre)
Rearrange the following in correct sequence pertaining to what is given within brackets at the end.
Axon endings - Dendrites - Axon - Perikaryon - Dendron (Neuron structur)
Rearrange the following in correct sequence pertaining to what is given within brackets at the end.
Diencephalon - Cerebellum - Medulla oblongata - Pons - Cerebrum - mid brain (sequence of parts of human brain).
Name the following:
Three types of neurons
Name the following:
Three types of nerves.
Name the following:
Three main parts of the neuron
Name three major divisions of the human nervous system.
Name the following:
Three layers of the meninges.
Name the three main parts of the human brain.
Name the following:
Two parts of the autonomic nervous system
Name the following:
Two types of reflexes.
Write full form of the following abbreviation:
CSF
Write full form of the following abbreviation:
CNS
Write full form of the following abbreviation:
PNS
Write full form of the following abbreviation:
ANS
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Define the following:
Neuron
Define the following term:
Nerve
Define stimulus.
Define the following term:
Synaptic cleft
Define the following:
Reflex action
Define the following term:
Corpus callosum
Differentiate between following pair with reference to the aspect in bracket.
cerebrum and cerebellum (function)
Distinguish between the following pair:
Sympathetic nervous system and parasympathatic nervous system (location and role)
Differentiate between following pair with reference to the aspect in bracket.
Sensory nerve and motor nerve (direction of impulse carried)
Differentiate between following pair with reference to the aspect in bracket.
cerebrum and spinal cord (arrangement of cytons and exons of neurons).
Differentiate between Spinal nerves and Cranial nerves (number of nerves).
Distinguish between the following pair:
Nerve impulse and flow of electricity (transmission and speed)
Differentiate between following pair with reference to the aspect in bracket.
medulla oblongata & cerebellum (function)
While watching a scary movie, mention its effects on the following organs by the autonomous nervous system in the table given below: (one has been done for you as an example).
| Organ | Sympathetic System | Parasympathetic System | |
| e.g. Lungs | Dilates bronchi and bronchioles | Constricts bronchi and bronchioles | |
| (1) | Heart | ______ | ______ |
| (2) | Pupil of the eye | ______ | ______ |
| (3) | Salivary gland | ______ | ______ |
Why do you call the spinal cord and the brain as the central nervous system?
Give reason:
Neurotransmitters are broken down by an enzyme just after passing an impulse from one neuron to the other.
Draw neat and labelled diagrams of a myelinated neuron
What are the advantages of having a nervous system?
What is the difference between reflex action and voluntary action?
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
Two hungry boys (A and B) enter a restaurant and see the menu. Boy B starts salivating but not A. Explain the reason for this difference.
The diagram below shows a section of the human brain and its associated parts. Answer the questions that follow:
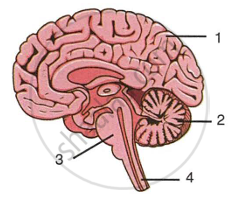 |
- Name the parts labeled 1, 2, 3 and 4.
- Name the protective membranous covering of the brain. Also mention its three layers.
- Name the basic unit of the brain.
- Write the important role of the part mentioned as 2.
The diagram given below shows the internal structure of a spinal cord depicting a phenomenon. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
 |
- Name the phenomenon shown in the figure and define the same.
- Identify the parts labelled as 1 and 2. Write one functional difference between these two.
- Name the bony protective covering and the membranous protective covering of the spinal cord.
- Label the guidelines 3 and 4.
- How is the labelled part 3 different from part 4 with respect to its composition (part of neuron)?
- Give the technical term for the point of contact between the two nerve cells.
- Name the fluid filled inside the central canal of spinal cord.
- Name the term used for a small gap between two neurons.
- Give one example of a neurotransmitter.
- Draw a neat diagram of a nerve cell and label the parts: Perikaryon, Node of Ranvier, Myelin sheath and Axon terminals.
The figure given below is the basic structural and functional unit of the human nervous system. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
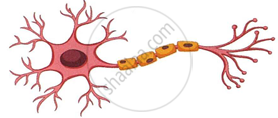 |
- Write the technical term for the diagram.
- Name two organs of our nervous system where these cells are richly found.
- How are these cells significant for us?
- Name the cell organelle that is absent in these cells and how does it affect our body metabolism?
- Redraw the same figure and label the following Perikaryon, Axon, Dendrites, Myelin sheath and Node of Ranvier.
Given below is the partially incomplete scheme of the components of peripheral nervous system. Fill up the blanks numbered (1)-(12):
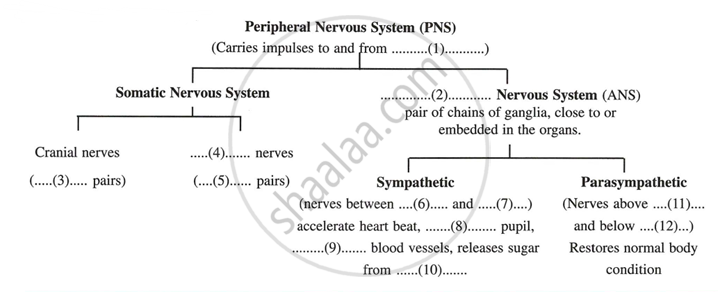
Solutions for 10: The Nervous System
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - The Nervous System Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - The Nervous System - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 - The Nervous System
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 10 (The Nervous System) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 10 The Nervous System are Major Division of the Nervous System, Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types, Human Nervous System, Nerve Fibres, The Spinal Cord, Reflex and Reflex Action, Transmission of Nerve Impulse, Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres, The Human Brain - Forebrain, Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), Types of Reflexes, Nervous Pathways in Reflexes, Reflex Arc, Complex Reflex Action, Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear, Major Division of the Nervous System, Neuron (Or Nerve Cell) and Its Types, Human Nervous System, Nerve Fibres, The Spinal Cord, Reflex and Reflex Action, Transmission of Nerve Impulse, Synapse - Properties of nerve fibres, The Human Brain - Forebrain, Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), Types of Reflexes, Nervous Pathways in Reflexes, Reflex Arc, Complex Reflex Action, Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear, Sense Organ, The Eyes, Human Eye, Working of the Human Eye, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Myopia Or Near-sightedness, Eye Defect and its Correction: Hypermetropia or Far-sightedness, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Presbyopia, Eye Defect and Its Correction: Astigmatism, Some Common Defects of the Eye, Stereoscopic (Binocular) Vision, Functions of the Ear, Human Ear.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions The Nervous System exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 10, The Nervous System Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
