Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
1: Cell - The structural and functional unit of life
2: Structure of chromosome, cell cycle and cell division
3: Genetics - Some Basic Fundamentals
Unit-2 : Plant Physiology
4: Absorption by roots - The Processes Involved
5: Transpiration
6: Photosynthesis
▶ 7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Unit-3 : Human Anatomy and Physiology
8: The Circulatory System
9: The Excretory System
10: The Nervous System
11: Sense Organ
12: The Endocrine System
13: The Reproductive System
Unit-4 : Human Evolution
14: Human Evolution
Unit-5 : Population
15: Population - The increasing numbers and rising problems
Unit-6 : Pollution
16: Pollution - A Rising Environmental Problem
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Chemical Coordination in Plants Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Chemical Coordination in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 7 of CISCE Selina for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE.
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE 7 Chemical Coordination in Plants Review Questions [Pages 89 - 91]
MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE
The only phytohormone which is a gas at ordinary temperature:
Ethane
Ethyl alcohol
Ethylene
Ethyne
The hormone which promotes the ripening of fruits is ______.
Auxins
Gibberellins
Cytokinins
Ethylene
A growth inhibiting hormone in plants:
Gibberellins
Indole-3 acetic acid
Abscisic Acid
Cytokinins
The hormone which stimulates cell division:
Auxins
Cytokinins
Gibberellins
Abscisic acid
Development of fruits without fertilisation is called ______.
Parthenogenesis
Parthenon
Parthenocarpy
Dormancy
The response by parts of the plant towards stimulus is called as ______.
Nastic movement
Tropism
Tactic movement
Senescence
Apical dominance is influenced by ______.
Gibberellins
Ethylene
Cytokinins
Auxins
The growth movement of plant parts which occurs due to touch stimulus is called ______.
Heliotropism
Chemotropism
Hydrotropism
Thigmotropism
The instrument which can be used to demonstrate geotropism is ______.
Manometer
Thermostat
Clinostat
Barometer
The hormone which accelerates senescence (ageing) and abscission of leaves is ______.
IAA
GA3
ABA
GA1
SHORT ANSWER TYPE
Match the items in column A with those of column B.
| Column A | Column B | ||
| (a) | Auxin | (i) | apical dominance |
| (b) | Gibberellin | (ii) | cell-division |
| (c) | Cytokinin | (iii) | fruit ripening |
| (d) | Ethylene | (iv) | internodal elongation |
Complete the following sentences:
Growth of root towards water is ______.
______ hormone inhibits apical dominance.
______ and ______ induce chemotropism of angiosperms and gymnosperms.
______ of sweet peas exhibit thigmotropism.
______ is also called as "stress hormone''.
How is movement in plants different from that in animals?
Name the stimulus which causes the following movement in plant:
phototropism
Name the stimulus which causes the following movement in plant:
Thigmotropism
Name the stimulus which causes the following movement in plant:
Hydrotropism
Name the stimulus which causes the following movement in plant:
Geotropism
Name the following:
Hormone that stimulates growth by cell division.
Name the following:
Growth-retarding hormone in plants.
Name the following:
The main auxin found in most plants.
DESCRIPTIVE TYPE
Define the following term:
Phytohormones
Define the following term:
Tropism
Define the following term:
Clinostat
Define the following term:
Apical dominance
Define the following term:
Parthenocarpy
Define the following term:
Abscission
Define the following term:
Heliotropism
List five plant growth hormones and briefly describe their roles.
Differentiate between:
Thigmotropism and geotropism
Differentiate between:
Positive and negative tropism
Differentiate between:
Stimulus and response
Differentiate between:
Phototropism and chemotropism
STRUCTURED/APPLICATION/SKILL TYPE
The tea plants are never allowed to grow lengthwise. This is done by cutting their apical buds, a process known as pruning. In this way, tea plants get a dense growth and easy yield. Answer the following questions:
- Name the scientific phenomenon that is being overcome by pruning.
- What plant hormone is responsible for the scientific phenomenon mentioned in (a)?
- Name one plant hormone which inhibits the said phenomenon.
The figure given below shows the stages of ripening in a banana. Answer the questions that follow:

- Name the plant hormone responsible for the above changes.
- Mention two characteristic features of this hormone.
The diagram given alongside shows a type of tropism. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
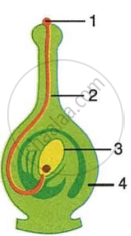
- Name and define the type of tropism shown in the diagram.
- Label the guidelines (1) to (4).
- Name two effective stimulants that help in the growth of part (2).
- Name two groups of plants where part (2) grows towards gametophyte with the help of the stimulants mentioned in (c).
Study the diagrams given below and answer the following questions:
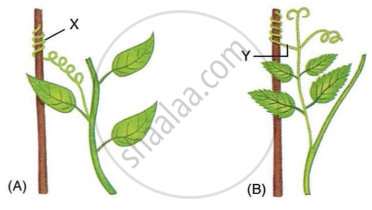
- Name the structures shown as X and Y in the figures (A) and (B), respectively.
- Write the functions performed by the structures X and Y.
- Name the phenomenon depicted and define it.
- How do the structures X and Y differ from each other?
- Give examples of the plants which show the said phenomenon.
Given below are the figures showing some kinds of tropic movements in plants. Study the same and answer the following questions:
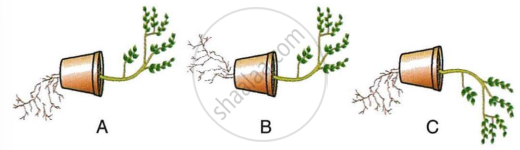
- Which one of these figures is correct? Give reason in support of your answer.
- Name the kinds of movements shown by the root system and shoot system. Define each.
- What are the two stimuli which affect root system and shoot system positively? Name them.
- Which of the following stimuli affects the growth of the root strongly?
- Gravity
- Water
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a pistil showing chemotropism in an angiospermic plant.
The box given below contains twelve words. Out of these, ten can be arranged in five suitable matching pairs. Make these five pairs in the form of a table.
| Auxins, Abscisic acid, Fruit ripening, Cytokinins, Closure of stomata, Parthenocarpy, Ethylene, Gibberellins, Tropism, Stem elongation, Cuscuta, Cell division. |
The figure given below depicts a kind of tropic movement in plants. Study the same and answer the following questions:
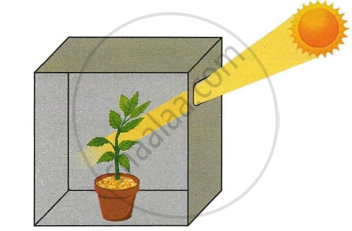
- What kind of a movement is shown in the figure? Define it.
- How does this movement differ from geotropism?
- Name the stimulus responsible for thigmotropism. Give one example of a plant showing thigmotropism.
- Name one stimulus which gives a positive response for the roots but a negative response for the shoot.
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of the part of a plant showing leaf tendril. Name the plant.
Solutions for 7: Chemical Coordination in Plants
![Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Chemical Coordination in Plants Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Chemical Coordination in Plants - Shaalaa.com](/images/concise-biology-english-class-10-icse_6:6250789d6fba4cd2aee862179baeada5.jpg)
Selina solutions for Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 - Chemical Coordination in Plants
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Selina solutions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE 7 (Chemical Coordination in Plants) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Selina textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE chapter 7 Chemical Coordination in Plants are Plant Hormones, Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins, Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins, Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins, Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene, Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA), Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants, Plant Hormones, Types of Plant Hormones: Auxins, Types of Plant Hormones: Gibberellins, Types of Plant Hormones: Cytokinins, Types of Plant Hormones: Ethylene, Types of Plant Hormones: Abscisic Acid (ABA), Coordination in Plant: Tropism in Plants.
Using Selina Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE solutions Chemical Coordination in Plants exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Selina Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE students prefer Selina Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 7, Chemical Coordination in Plants Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Concise Biology [English] Class 10 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
