Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Differentiate between the following:
Turgor pressure and wall pressure
Solution
| Turgor Pressure | Wall Pressure | ||
| 1. | The hydrostatic pressure that endosmosis creates against the cell wall is known as turgor pressure. | 1. | The force that the cell wall exerts against turgor pressure is known as wall pressure. |
| 2. | Turgor pressure acts on the cell wall. | 2. | Cell wall pressure is generated by the cell wall. |
| 3. | Turgor pressure keeps plant stems upright, expands leaves and aids in the opening and closing of stomata, among other things. | 3. | Wall pressure maintains cell and plant structure. |
| 4. | The direction of Turgor pressure is towards the outside. | 4. | The direction of wall pressure is towards the inside of the cell. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain Turgor pressure
The diagram below represents a process in plants. The setup was placed in bright sunlight. Answer the following questions:

a) Name the physiological process depicted in the diagram.
Why was oil added to the water?
b) When placed in bright sunlight for four hours, what do you observe with regard to the initial and final weight of the plant? Give a suitable reason for your answer
c) What happens to the level of water when this setup is placed in:
- Humid conditions?
- Windy conditions?
d) Mention any three adaptations found in plants to overcome the process mentioned in (i).
e) Explain the term ‘Guttation’.
Give the equivalent term for the following:
The condition in which the cell contents are shrunken.
Give the equivalent terms for the following:
Loss of water through a cut stem.
Give reason for the following:
It is better to transplant seedlings in a flower-bed in the evening and not in the morning.
Fill in the Blank
Wilting and drooping of leaves is due to loss of ________.
Excessive use of fertilisers in agricultural fields reduces the yield of crops. Justify the statement.
The hydrostatic pressure of the cell sap on the cell wall is called ______.
When the cells of a plant are fully distended, the condition is called ______.
Given below is the figure of a plant cell showing different kinds of pressure acting upon it. Study the figure and answer the questions that follow:
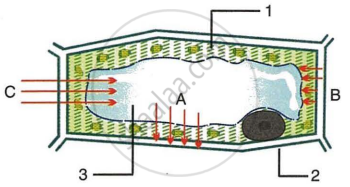
- In the figure, 1, 2 and 3 represent:
- Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Vacuole respectively
- Vacuole, Cytoplasm, Cell wall respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell membrane and vacuole respectively.
- Cytoplasm, Cell wall and Vacuole respectively.
- B in the figure represents:
- Osmotic pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Wall pressure
- Diffusion pressure
- A in the figure represents:
- irnbibition pressure
- Wall pressure
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- C in the figure represents:
- Turgor pressure
- Osmotic pressure
- Wall pressure
- Imbibition pressure
- Draw a neat and labelled diagram of a plasmolyzed plant cell.
