Advertisements
Chapters
2: Fundamentals of Genetics
▶ 3: Absorption by Roots
4: Transpiration
5: Photosynthesis
6: The Circulatory System
7: The Excretory System
8: The Nervous System and Sense Organs
9: The Endocrine System
10: The Reproductive System
11: Human Population
12: Physical Health and Hygiene
13: Pollution
![ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Absorption by Roots ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Absorption by Roots - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3: Absorption by Roots
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3 of CISCE ICSE for Biology [English] Class 10.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Short Questions
How is root hair structurally adapted for absorption of water from the soil?
Root hairs become flaccid, when fertilizers are added to the moist soil around it. Explain.
What do you mean by transpiration pull ?
Define the Cohesive and Adhesive forces.
Give at least three uses of water to green plants
What is toxicity ?
Grapes shrink when immersed in a very strong sugar solution.” Explain.
What is the significance of diffusion?
What is the water potential?
A few RBC’s were kept in three test tubes containing isotonic, hypotonic and hypertonic solutions. What will be the expected observations after a few hours? Explain.
Explain why the grass in your lawn becomes greener if you add a little fertilizer to it, but it dies if you add a lot of it.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Give Reasons
Give Reasons for the following.
It is necessary to maintain a normal osmotic concentration of the blood.
Give Reasons for the following.
Salt and sugar are used in preserving food.
Give Reasons for the following.
On sprinkling common salt on grass growing in a lawn, the grass is killed.
Give Reasons for the following.
The raisins swell up in the water.
Give Reasons for the following.
We gargle with saline water in case of throat infection.
Explain why:
The leaves of wilted lettuce, if kept in cold water, become crisp.
Explain why:
Bacteria and fungi do not grow in pickles, jams, jellies and squashes.
Give Reasons for the following.
Freshwater fish cannot survive in seawater.
Give Reasons for the following.
A closed can of dried seeds bursts open if some water enters it by accident.
Give Reasons for the following.
Drops of water on a leaf of plant like peepal does not enter the leaf by osmosis?
Give Reasons for the following.
Plants growing in fertilized soil are often found to wilt if the soil is not adequately watered. Why?
Give Reasons for the following.
Plants begin to die when the excess of soluble fertilizers are added to the soil?
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Differentiate
Differentiate between:
Osmosis and Diffusion
Differentiate between:
Turgid and Flaccid.
Differentiate between the following
Permeable and Semi-permeable membrane.
Differentiate between the following
Active transport and Passive transport.
Differentiate between the following:
Turgor pressure and wall pressure
Differentiate between the following
Turgor pressure and Root pressure
Differentiate between the following:
Plasmolysis and Deplasmolysis.
Differentiate between the following
Endosmosis and Exosmosis
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Diagram Based Questions
In the figure below ‘A’ shows a cell in the normal state and ‘B’ shows the same cell after leaving it in a certain solution for a few minutes.

(i) Describe the change which has occurred in the cell as seen in B.
(ii) Give the technical term for the condition of the cell as reached in B and as it was in A.
(iii) Define the process which led to this condition.
(iv) What was the solution-isotonic, hypotonic or hypertonic, in which the cell was kept?
(v) How can the cell in B, be brought back to its original condition?
(vi) Name the parts numbered 1 to 3.
The alongside diagram A shows a root hair growing through the soil particles. Diagram B is the root hair of an aquatic plant.
(i) Name the parts 1,2,3.
(ii) Name two substances which enter the root hair. What are their uses?
(iii) By what process do these substances enter the root hair?
(iv) Account for the different shapes of root hairs in the two diagrams.
Given below is the diagram of a cell as seen under the microscope after having been placed in a solution:

(i) What is the technical term used for the state/condition of the cell given above?
(ii) Give the technical term for the solution in which the cell was placed.
(iii) Name the parts numbered 1 to 4.
(iv) Is the cell given above a plant cell or an animal cell ? Give two reasons in support of your answer as evident from the diagram.
(v) What would you do to bring this cell back to its original condition?
The below diagram represents a plant cell after being placed in a strong sugar solution. Guidelines 1 to 5 indicate the following: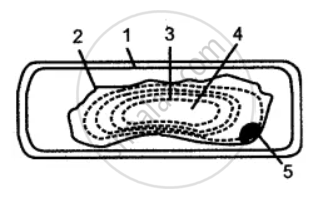
1. Cell wall
2. Plasma membrane.
3. Protoplasm
4. Large vacuole
5. Nucleus
Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow :
(i) What is the state of the cell shown in the diagram?
(ii) Name the structure which acts as a selectively permeable membrane.
(iii) If the cell had been placed in distilled water instead of a strong sugar solution which features: would not have been present?
(iv) If the cell in the diagram possessed chloroplasts where would these be present?
(v) Name any one feature of this plant cell which is not present in animal cells.
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of a part of the cross-section of the root in the root hair zone. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow :
(i) Name the parts indicated by guidelines ‘1’ to ‘5’
(ii) Is the root hair cell unicellular or multi-cellular?
(iii) Draw a labeled diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it.
(iv) Name the process responsible for the entry of water molecules from the soil into A1 and then A2.
(v) What pressure is responsible for the movement of water in the direction indicated by arrows?
(vi) How is this pressure set up?
The below figure shows a root hair:
(i) Label the parts 1 to 4.
(ii) What is the role of part 4?
(iii) Why is the root hair one-celled?
(iv) What will happen to the root hair if some fertilizer is added to the soil near the root hair?
The diagram given below is of an experiment just at the start. Study the diagram carefully and answer the following questions :
(i) What does the experiment demonstrate?
(ii) Define, the process demonstrated in the experiment.
(iii) What changes are observed after a few hours?
(iv) Give two examples of a semi-permeable membrane.
(v) Which limb of the U-tube contains a more concentrated sucrose solution, A or B?
(vi) Why is the membrane separating the two solutions labeled as semi-permeable membrane?
A plant cell kept in a drop of water was examined under the low power magnification of a microscope, as shown:
(i) What would you do to bring this cell back to its original condition?
(ii) What scientific term is used for such condition?
(iii) Draw the same cell if it is kept in a strong sugar solution.
The apparatus arranged here signifies an important process.
(i) Name the process.
(ii) Where does this process occur in plants?
(iii) What solution is placed inside the dialysis tubing?
(iv) What happens to the level of the solution in the capillary tube?
(v) Define the process mentioned in Q. (i) above.
Given below is the figure of an experimental set up to demonstrate root pressure.
(i) Define root pressure.
(ii) What change would you observe in the water level after some time?
(iii) What role is being played by the root pressure in the given experiment?
(iv) Why the oil has been sprinkled on water?
The diagram given below represents the result of an experiment conducted on two freshly taken shoots of a green herbaceous plant. The lower ends dip in the water.
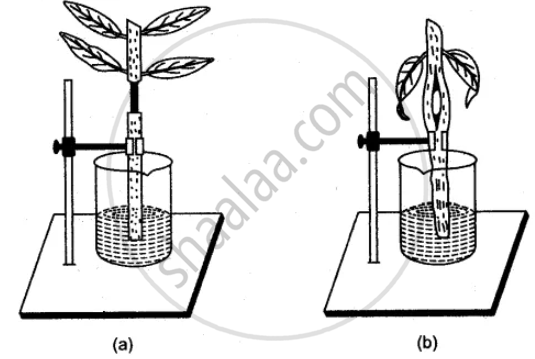
(i) What is the aim of the experiment?
(ii) Some parts of the stem in both the shoots have been removed. Name the conducting tissue in shoot A and in shoot B, that has been removed.
(iii) What are the results of this experiment?
A thin strip of epidermal cells from the fleshy scales of an onion bulb was examined in a drop of water, under a microscope. All the epidermal cells looked alike and the figure alongside represents one of them. The thin strip was then transferred to a drop of strong sugar solution and re-examined under the microscope after about five minutes.

(i) Make a sketch of one of the epidermal cells, as it might appear after immersion in a strong sugar solution. Label any two parts which have undergone a change.
(ii) Give the scientific term for the change shown in Q.(i) above.
(iii) What would you do to bring this cell back to its original condition?
(iv) Give the scientific term used for the recovery of the cell as a result of the step taken in Q.(iii) above.
Given below is an experimental demonstration.
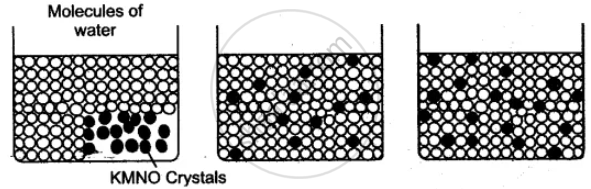
(i) Which phenomenon has been demonstrated in the given figure?
(ii) What is the solute and what is solvent in the above experiment?
(iii) Define the phenomenon in Q. (i) above.
(iv) Give one example from your daily life experiences based on this principle.
In an experiment, two sets of apparatus were set up as shown below:
In A there is a concentrated sugar solution inside the thistle funnel and red ink in the water outside the funnel. In B there is a concentrated glucose solution with red ink inside the thistle funnel and water outside the thistle funnel.
In both A and B the level of liquid inside the funnels rises up the tubes. In A the sugar solution turns red and in B, the water turns red.
Study the given observations and answer these questions:

- Name the process by which red ink moves in A and B.
- Which type of pressure forces the water molecules to move towards thistle funnels and cause a rise in the water level?
- Where does this process occur in plants and animals?
- What material could be used as a semi-permeable membrane?
The beaker is divided into two chambers A and B. The big circle represents solute and the small circles solvent.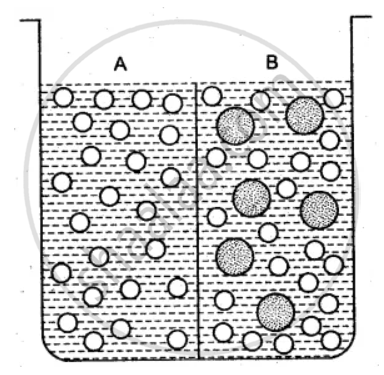
(i) What can you say about the size of the holes in the membrane, if it is to behave semi- permeably between these two?
(ii) Will the solvent molecules pass through the membrane from left to right, from right to left, in either direction or in both directions?
(iii) In which direction will there be a net movement of solvent molecules?
A complete ring of bark was removed from a tree in spring. The tree continued to live through summer but a swelling appeared on the bark above the ring while the bark below shriveled up. Answer the questions given below :
(i) Account for the swelling in the bark above the ring.
(ii) Account for the shrinking of the bark below the ring.
(iii) Name the tissue that distributes food in plants.
(iv) Name the tissue that distributes water in plants.
(v) What is the role of a bark in a plant?
The diagram below represents an experimental set up to demonstrate a vital process. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the process.
(ii) Define the above named process.
(iii) What would you observe in the experimental setup after an hour or so?
(iv) What control experiment can be set up for the above experiment?
(v) Keeping in mind the root hair cell and its surrounding name the part that corresponds to (1) Concentrated sugar solution, (2) Parchment paper, (3) Water in the beaker.
(vi) Name any other substance that can be used instead of parchment paper in the above experiment.
(vii) Mention two advantages of this process to the plant.
A candidate in order to study the process of osmosis has taken 3 potato cubes and put them in 3 different beakers containing 3 different solutions. After 24 hours, in the first beaker the potato cube increased in size, in the second beaker the potato cube decreased in size and in the third beaker there was no change in the size of the potato cube. The following diagram shows the result of the same experiment:

(i) Give the technical terms of the solutions used in beakers, 1, 2 and 3.
(ii) In beaker 3, the size of the potato cube remains the same. Explain the reason in brief.
(iii) Write the specific feature of the cell sap of root hairs which helps in absorption of water.
(iv) What is osmosis?
(v) How does a cell wall and a cell membrane differ in their permeability?
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Sketch and Label the Diagram
Give a diagrammatic representation of plasmolysis in a cell.
Draw a cross-section of root showing association of soil particles with root hairs.
Draw a diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear when a concentrated solution of fertilizers is added near it.
A thin strip of epidermal cells of a leaf was observed in a drop of water. They all looked turgid and normal.
(a) Draw a diagram of such a cell.
(b) Draw a diagram of a cell if this strip is transferred to a strong concentrated solution of sugar. What is term used for the effect on the cells ?
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Explain the Terms
Explain the Term: Diffusion
Explain the Term: Osmosis
Explain the Term: Endosmosis
Explain the Term: Exosmosis
Explain the Term: Plasmolysis
Explain the Term: Guttation
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Name the Following
Name the following:
Water is absorbed from the soil by which part.
Name the following:
The kind of cells that constitute the cortex of a root.
Name the following:
The pressure through which water can rise upto some feet.
Name the following:
Root hairs are the extension of which cells.
Name the following:
The movement of a liquid through a selectively permeable membrane.
Name the following:
Name the process by which water enters the root hair cell.
Name the following:
The process by which raisins swell up when placed in a beaker of water.
Name the following:
The membrane which allows water molecules to pass through, but not sugar molecules.
Name the following:
The inward movement of solvent molecules through the plasma membrane of the cell.
Name the following:
The solution outside the cell having lower solute concentration than the fluids.
Name the following:
The process by which wilting or drooping of leaves occurs.
Name the following:
The condition in which the contents of a cell exert pressure against the cell wall making it distended.
Name the following:
Condition of cell in which the cell content are shrunken.
Name the following:
Movement of ions from the region of lower concentration to higher concentration by using energy (ATP).
Name the following:
Name the process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Give Technical Terms
Give Technical Term for the following.
Phenomenon of absorption of water by surface attraction.
Give Technical Term for the following.
Solutions which have the same osmotic pressure.
Give Technical Term for the following.
A solution whose concentration is equal to the cell sap.
Give Technical Term for the following.
A solution whose concentration is greater than that of the cell sap.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The pressure which is responsible for the movement of water molecules across the cortical cells of the root.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The condition in which the water from a cell is completely removed due to exosmosis and no more shrinkage is possible.
Give Technical Term for the following.
A cell in a fully extended condition.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The pressure exerted by cell contents on a plant cell wall.
Name the following:
The condition of a cell placed in a hypotonic solution.
Fill in the Blanks
Osmosis in the diffusion of _______ molecules from the region of higher _____ potential to that of lower potential across a S.P.M.
Give Technical Term for the following.
Tissue which transports manufactured food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
Give Technical Term for the following.
The tissue responsible for the ascent of sap in plants.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Fill in the Blanks
Fill in the Blank
The pressure which develops in the cortical cells of root which force a part of the water upward ____________.
Fill in the Blank
Leaves get wilted if _________ is removed from the plant.
Fill in the Blank
______ serves as a medium for the transport of inorganic salts and food molecules in the plant.
Fill in the Blank
When there is no movement of water in the cell from the outside medium, the medium is considered to be ______ to cell sap.
Fill in the Blank
A plasmolysed cell has __________ protoplast.
Fill in the Blank
Raisin swells up when kept in a __________ solution.
Fill in the Blank
Water and mineral salts absorbed by root is known as ______.
Fill in the Blank
The condition opposite to turgid is ___________.
Fill in the Blanks
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a region of their ________ concentration to the region of their ________ concentration.
Fill in the Blank
Wilting and drooping of leaves is due to loss of ________.
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots True and False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Xylem is the water-conducting tissue in plants.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Osmosis is defined as the movement of water from a concentrated sugar solution to a dilute sugar solution.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
The plasma membrane permits the passage of all solutes and water.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
During exosmosis, water moves from inside the cell to the outside of the cell.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Plasmolysis makes the cell turgid.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Cells that have lost their water content are said to be deplasmolysed.
True
False
Mention, if the following statement is True or False. If false rewrite the wrong statement in its correct form:
Flaccidity is the reverse of turgidity.
True
False
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Multiple Choice Questions
Multiple Choice Question:
In the process of osmosis in a cell:
Both protoplasm and cell wall act as a membrane
Only cell wall acts as a membrane
Only outermost layer of protoplast acts as a membrane
The entire protoplast acts as a membrane
Multiple Choice Question:
Osmosis involves:
Cell to cell movement of water
Movement of water through cortical cells
Adiva absorption of water through roots
All of the above
Multiple Choice Question:
Plasma membrane controls:
Passage of water only
Passage of water and solutes in and out of the cell
Passage of water and solutes into the cell
Movement of cell contents out of the cell
The space between the cell wall and plasma membrane in a plasmolysed cell is filled with ______.
isotonic solution
hypotonic solution
hypertonic solution
water
Multiple Choice Question:
Seeds when soaked in water imbibe in it because:
Osmotic pressure inside the seed is low
Seed coat contains lot of salts
The process of absorption works
There are many vacuoles in the endosperm
Multiple Choice Question:
Process of endosmosis stops:
When equal
When solution becomes isotonic
When the leaves fall.
When there is no light
Multiple Choice Question:
Marine fish when thrown under tap water bursts because of:
Endosmosis
Diffusion
Exosmosis
Plasmolysis
Choose the correct answer:
Osmosis involves diffusion of ___________
suspended particles from lower concentration to higher concentration.
suspended particles from higher concentration to lower concentration.
Molecules or ions from the more concentrated solution to the less concentrated solution.
water from the less concentrated solution to the more concentrated solution.
Multiple Choice Question:
Water will be absorbed by the root hairs when:
Concentration of solutes in the cell sap is high
Concentration of solutes in the soil is high
The plant is rapidly respiring
None of the above
Multiple Choice Question:
When a plant wilts, the sequence of events will be as follows:
Exosmosis, plasmolysis, deplasmolysis, temporary wilting
Exosmosis, deplasmolysis, plasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting
Exosmosis, plasmolysis, temporary and permanent wilting
None of the above
Multiple Choice Question:
When cell is fully turgid, which of the following will be zero?
Osmotic pressure
Turgor pressure
Wall pressure
Suction pressure (SP) or diffusion pressure deficit (DPD)
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 3 Absorption by Roots Match the Column
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Diffusion | (a) The exit or flow of water from the cell to the outer environment. |
| (ii) Xylem | (b) The shrinkage of protoplasm when the cell is kept in a hypertonic solution. |
| (iii) Root pressure | (c) The tissue through which water and mineral salts move upward in a plant. |
| (iv) Isotonic solution | (d) Two solutions which have equal osmotic pressure. |
| (v) Exosmosis | (e) The process by which the molecules of perfume spread in the room when the bottle is open. |
| (vi) Osmosis | (f) The process by which roots absorb water from the soil. |
| (vii) Plasmolysis | (g) The pressure by which water rises up to some feet in a lofty tree. |
| (viii) Hypotonic solution | (h) The concentration of the solution when lower than that of the cell sap. |
Solutions for 3: Absorption by Roots
![ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Absorption by Roots ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Absorption by Roots - Shaalaa.com](/images/biology-english-class-10_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
ICSE solutions for Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 3 - Absorption by Roots
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Biology [English] Class 10 CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. ICSE solutions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 10 CISCE 3 (Absorption by Roots) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. ICSE textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Biology [English] Class 10 chapter 3 Absorption by Roots are Plant Anatomy and Plant Physiology, Characteristics of Roots for Absorbing Water, Concept of Osmosis, Semi-permeable Membrane (Cell Membrane), Concept of Imbibition, Simple Diffusion, Osmotic Pressure, Turgidity and Flaccidity (Plasmolysis), Root Pressure, Translocation of Water (Ascent of Sap), Water absorbing organ, Need of Water and Minerals for Plant, Active Transport, Means of Transport in Plants.
Using ICSE Biology [English] Class 10 solutions Absorption by Roots exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in ICSE Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Biology [English] Class 10 students prefer ICSE Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3, Absorption by Roots Biology [English] Class 10 additional questions for Mathematics Biology [English] Class 10 CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
